Comparative Sensing and Judgment Control System for Temperature Maintenance for Optimal Treatment in Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy Surgery
- PMID: 38257692
- PMCID: PMC10821041
- DOI: 10.3390/s24020596
Comparative Sensing and Judgment Control System for Temperature Maintenance for Optimal Treatment in Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy Surgery
Abstract
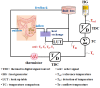
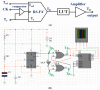
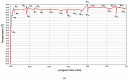
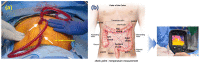
For tumors wherein cancer cells remain in the tissue after colorectal cancer surgery, a hyperthermic anticancer agent is injected into the abdominal cavity to necrotize the remaining cancer cells with heat using a hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy system. However, during circulation, the processing temperature is out of range and the processing result is deteriorated. This paper proposes a look-up table (LUT) module design method that can stably maintain the processing temperature range during circulation via feedback. If the temperature decreases or increases, the LUT transmits a command signal to the heat exchanger to reduce or increase heat input, thereby maintaining the treatment temperature range. The command signal for increasing and decreasing heat input is Tp and Ta, respectively. The command signal for the treatment temperature range is Ts. If drug temperatures below 41 and above 43 °C are input to the LUT, it sends a Tp or Ta signal to the heat exchanger to increase or decrease the input heat, respectively. If the drug's temperature is 41-43 °C, the LUT generates a Ts signal and proceeds with the treatment. The proposed system can automatically control drug temperature using temperature feedback to ensure rapid, accurate, and safe treatment.
Keywords: automatic temperature control; cancer surgery; comparator; look-up table; thermal chemotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures









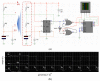
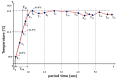
Similar articles
-
The Design of an Automatic Temperature Compensation System through Smart Heat Comparison/Judgment and Control for Stable Thermal Treatment in Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC) Surgery.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jul 27;23(15):6722. doi: 10.3390/s23156722. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37571507 Free PMC article.
-
The Temperature-Dependent Effectiveness of Platinum-Based Drugs Mitomycin-C and 5-FU during Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC) in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines.Cells. 2020 Jul 25;9(8):1775. doi: 10.3390/cells9081775. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32722384 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the thermal stability of nab-paclitaxel during hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023 Mar 1;24(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40360-023-00653-2. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36859304 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy for Colorectal Peritoneal Metastases: A Systematic Review.Dis Colon Rectum. 2022 Jan 1;65(1):16-26. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0000000000002315. Dis Colon Rectum. 2022. PMID: 34636780
-
Hyperthermic intraoperative peritoneal chemotherapy and cytoreductive surgery for people with peritoneal metastases: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Sep;28(51):1-139. doi: 10.3310/KWDG6338. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39254852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yoon K., Chung J.-W., Kim K.G. A Metal Detector for Clip Location Tracking of Stomach and Colon Cancer during Laparoscopic Surgery. Appl. Sci. 2022;12:7330. doi: 10.3390/app12147330. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

