Transcriptome Profiling of Oncorhynchus mykiss Infected with Low or Highly Pathogenic Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus (VHSV)
- PMID: 38257883
- PMCID: PMC10821180
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12010057
Transcriptome Profiling of Oncorhynchus mykiss Infected with Low or Highly Pathogenic Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus (VHSV)
Abstract
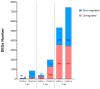
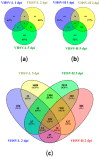
The rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) is the most important produced species in freshwater within the European Union, usually reared in intensive farming systems. This species is highly susceptible to viral hemorrhagic septicemia (VHS), a severe systemic disease widespread globally throughout the world. Viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) is the etiological agent and, recently, three classes of VHSV virulence (high, moderate, and low) have been proposed based on the mortality rates, which are strictly dependent on the viral strain. The molecular mechanisms that regulate VHSV virulence and the stimulated gene responses in the host during infection are not completely unveiled. While some preliminary transcriptomic studies have been reported in other fish species, to date there are no publications on rainbow trout. Herein, we report the first time-course RNA sequencing analysis on rainbow trout juveniles experimentally infected with high and low VHSV pathogenic Italian strains. Transcriptome analysis was performed on head kidney samples collected at different time points (1, 2, and 5 days post infection). A large set of notable genes were found to be differentially expressed (DEGs) in all the challenged groups (e.s. trim63a, acod1, cox-2, skia, hipk1, cx35.4, ins, mtnr1a, tlr3, tlr7, mda5, lgp2). Moreover, the number of DEGs progressively increased especially during time with a greater amount found in the group infected with the high VHSV virulent strain. The gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis highlighted that functions related to inflammation were modulated in rainbow trout during the first days of VHSV infection, regardless of the pathogenicity of the strain. While some functions showed slight differences in enrichments between the two infected groups, others appeared more exclusively modulated in the group challenged with the highly pathogenic strain.
Keywords: NGS; RNA-Seq; VHS; pathogenicity; rainbow trout; transcriptomic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- WOAH . Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals. WOAH; Paris, France: 2021. Infection with viral haemorrhagic septicemia virus.
-
- Béarzotti M., Monnier A.F., Vende P., Grosclaude J., de Kinkelin P., Benmansour A. The glycoprotein of viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV): Antigenicity and role in virulence. Vet. Res. 1995;26:413–422. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

