Urine proteomic signatures of histological class, activity, chronicity, and treatment response in lupus nephritis
- PMID: 38258904
- PMCID: PMC10906224
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.172569
Urine proteomic signatures of histological class, activity, chronicity, and treatment response in lupus nephritis
Abstract
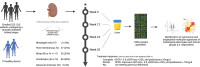
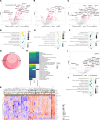
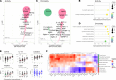
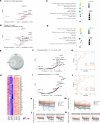
Lupus nephritis (LN) is a pathologically heterogenous autoimmune disease linked to end-stage kidney disease and mortality. Better therapeutic strategies are needed as only 30%-40% of patients completely respond to treatment. Noninvasive biomarkers of intrarenal inflammation may guide more precise approaches. Because urine collects the byproducts of kidney inflammation, we studied the urine proteomic profiles of 225 patients with LN (573 samples) in the longitudinal Accelerating Medicines Partnership in RA/SLE cohort. Urinary biomarkers of monocyte/neutrophil degranulation (i.e., PR3, S100A8, azurocidin, catalase, cathepsins, MMP8), macrophage activation (i.e., CD163, CD206, galectin-1), wound healing/matrix degradation (i.e., nidogen-1, decorin), and IL-16 characterized the aggressive proliferative LN classes and significantly correlated with histological activity. A decline of these biomarkers after 3 months of treatment predicted the 1-year response more robustly than proteinuria, the standard of care (AUC: CD206 0.91, EGFR 0.9, CD163 0.89, proteinuria 0.8). Candidate biomarkers were validated and provide potentially treatable targets. We propose these biomarkers of intrarenal immunological activity as noninvasive tools to diagnose LN and guide treatment and as surrogate endpoints for clinical trials. These findings provide insights into the processes involved in LN activity. This data set is a public resource to generate and test hypotheses and validate biomarkers.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Diagnostics; Lupus; Nephrology; Proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UH2 AR067685/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UM2 AR067678/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI168450/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067688/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067689/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067690/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067677/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067694/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR069572/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067679/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR074096/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK134625/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067681/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR073750/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067676/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067691/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

