The determinants of COVID-induced brain dysfunctions after SARS-CoV-2 infection in hospitalized patients
- PMID: 38260018
- PMCID: PMC10800467
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1249282
The determinants of COVID-induced brain dysfunctions after SARS-CoV-2 infection in hospitalized patients
Abstract
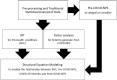
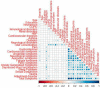
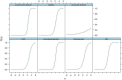
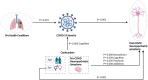
The severity of the pandemic and its consequences on health and social care systems were quite diverse and devastating. COVID-19 was associated with an increased risk of neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders after SARS-CoV-2 infection. We did a cross-sectional study of 3 months post-COVID consequences of 178 Cuban subjects. Our study has a unique CUBAN COVID-19 cohort of hospitalized COVID-19 patients and healthy subjects. We constructed a latent variable for pre-health conditions (PHC) through Item Response Theory (IRT) and for post-COVID neuropsychiatric symptoms (Post-COVID-NPS) through Factor Analysis (FA). There seems to be a potential causal relationship between determinants of CIBD and post-COVID-NPS in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. The causal relationships accessed by Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) revealed that PHC (p < 0.001) and pre-COVID cognitive impairments (p < 0.001) affect the severity of COVID-19 patients. The severity of COVID-19 eventually results in enhanced post-COVID-NPS (p < 0.001), even after adjusting for confounders (age, sex, and pre-COVID-NPS). The highest loadings in PHC were for cardiovascular diseases, immunological disorders, high blood pressure, and diabetes. On the other hand, sex (p < 0.001) and pre-COVID-NPS including neuroticism (p < 0.001), psychosis (p = 0.005), cognition (p = 0.036), and addiction (p < 0.001) were significantly associated with post-COVID-NPS. The most common neuropsychiatric symptom with the highest loadings includes pain, fatigue syndrome, autonomic dysfunctionalities, cardiovascular disorders, and neurological symptoms. Compared to healthy people, COVID-19 patients with pre-health comorbidities or pre-neuropsychiatric conditions will have a high risk of getting severe COVID-19 and long-term post-COVID neuropsychiatric consequences. Our study provides substantial evidence to highlight the need for a complete neuropsychiatric follow-up on COVID-19 patients (with severe illness) and survivors (asymptomatic patients who recovered).
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; long-COVID; neuropsychology; post-COVID neuropsychiatric symptoms/disorders.
Copyright © 2024 Yasir, Jin, Razzaq, Caballero-Moreno, Galán-García, Ren, Valdes-Sosa, Rodriguez-Labrada, Bringas-Vega and Valdes-Sosa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Psychiatric and neuropsychiatric presentations associated with severe coronavirus infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis with comparison to the COVID-19 pandemic.Lancet Psychiatry. 2020 Jul;7(7):611-627. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30203-0. Epub 2020 May 18. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32437679 Free PMC article.
-
Post-COVID-19 Symptoms 2 Years After SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Hospitalized vs Nonhospitalized Patients.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Nov 1;5(11):e2242106. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42106. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 36378309 Free PMC article.
-
New‑onset neuropsychiatric sequelae and 'long‑COVID' syndrome (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2022 Oct 4;24(5):705. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11641. eCollection 2022 Nov. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 36324612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mid and long-term neurological and neuropsychiatric manifestations of post-COVID-19 syndrome: A meta-analysis.J Neurol Sci. 2022 Mar 15;434:120162. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2022.120162. Epub 2022 Jan 29. J Neurol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35121209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estimated Global Proportions of Individuals With Persistent Fatigue, Cognitive, and Respiratory Symptom Clusters Following Symptomatic COVID-19 in 2020 and 2021.JAMA. 2022 Oct 25;328(16):1604-1615. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.18931. JAMA. 2022. PMID: 36215063 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
IL-8 (CXCL8) Correlations with Psychoneuroimmunological Processes and Neuropsychiatric Conditions.J Pers Med. 2024 May 3;14(5):488. doi: 10.3390/jpm14050488. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38793070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Nsp7 plays a role in cognitive dysfunction by impairing synaptic plasticity.Front Neurosci. 2024 Nov 21;18:1490099. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1490099. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39640294 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

