Preparation and characterization of lignin-derived carbon aerogels
- PMID: 38260044
- PMCID: PMC10801266
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1326454
Preparation and characterization of lignin-derived carbon aerogels
Abstract
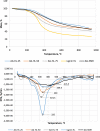
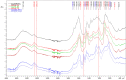
Lignin is considered a valuable renewable resource for building new chemicals and materials, particularly resins and polymers. The aromatic nature of lignin suggests a synthetic route for synthesizing organic aerogels (AGs) similar to the aqueous polycondensation of resorcinol with formaldehyde (FA). The structure and reactivity of lignin largely depend on the severity of the isolation method used, which challenges the development of new organic and carbon materials. Resorcinol aerogels are considered a source of porous carbon material, while lignin-based aerogels also possess great potential for the development of carbon materials, having a high carbon yield with a high specific surface area and microporosity. In the present study, the birch hydrolysis lignin and organosolv lignin extracted from pine were used to prepare AGs with formaldehyde, with the addition of 5-methylresorcinol in the range of 75%-25%, yielding monolithic mesoporous aerogels with a relatively high specific surface area of up to 343.4 m2/g. The obtained lignin-based AGs were further used as raw materials for the preparation of porous carbon aerogels (CAs) under well-controlled pyrolysis conditions with the morphology, especially porosity and the specific surface area, being dependent on the origin of lignin and its content in the starting material.
Keywords: aerogels; carbon aerogels; lignin; pyrolysis; resorcinol–formaldehyde gels; supercritical drying.
Copyright © 2024 Jõul, Järvik, Lees, Kallavus, Koel and Lukk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of Organosolv Lignins and Their Application in the Preparation of Aerogels.Materials (Basel). 2022 Apr 13;15(8):2861. doi: 10.3390/ma15082861. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35454554 Free PMC article.
-
Ferrocene Introduced into 5-Methylresorcinol-Based Organic Aerogels.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Jul 16;12(7):1582. doi: 10.3390/polym12071582. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32708747 Free PMC article.
-
Pore size controllable preparation for low density porous nano-carbon.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2013 Oct;13(10):7012-5. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2013.8063. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2013. PMID: 24245178
-
Resorcinol-Formaldehyde-Derived Carbon Xerogels: Preparation, Functionalization, and Application Aspects.Materials (Basel). 2023 Oct 5;16(19):6566. doi: 10.3390/ma16196566. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37834703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review on the preparation and application of lignin-based carbon aerogels.RSC Adv. 2022 Apr 7;12(17):10755-10765. doi: 10.1039/d2ra01402e. eCollection 2022 Mar 31. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35424986 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lignin Polyurethane Aerogels: Influence of Solvent on Textural Properties.Gels. 2024 Dec 14;10(12):827. doi: 10.3390/gels10120827. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39727586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brebu M., Vasile C. (2010). Thermal degradation of lignin—a Review. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 44, 353–363.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

