Explaining Long COVID: A Pioneer Cross-Sectional Study Supporting the Endocrine Hypothesis
- PMID: 38260089
- PMCID: PMC10801829
- DOI: 10.1210/jendso/bvae003
Explaining Long COVID: A Pioneer Cross-Sectional Study Supporting the Endocrine Hypothesis
Abstract
Context: In some patients, symptoms may persist after COVID-19, defined as long COVID. Its pathogenesis is still debated and many hypotheses have been raised.
Objective: Our primary objective was to evaluate the corticotroph and somatotroph functions of patients previously infected with SARS-CoV-2 and experiencing post-COVID-19 syndrome to detect any deficiencies that may explain long COVID.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted including patients who had previously contracted SARS-CoV-2 with a postinfection period of 3 months or less to 15 months, divided into 2 groups. The first group (G1) comprised fully recovered patients, while the second group (G2) included patients experiencing long COVID. The primary outcome was the comparison of corticotroph and somatotroph functions.
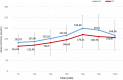
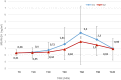
Results: A total of 64 patients were divided into 2 groups, each consisting of 32 patients. G2 exhibited more frequently anterior pituitary deficits compared to G1 (P = .045): for the corticotroph axis (G1: 6.3% vs G2: 28.1%) and for the somatotroph axis (G1: 31.3% vs G2: 59.4%). Baseline cortisol level was significantly lower in G2 (G1: 13.37 µg/dL vs G2: 11.59 µg/dL) (P = .045). The peak cortisol level was also lower in G2 (G1: 23.60 µg/dL vs G2: 19.14 µg/dL) (P = .01). For the somatotroph axis, the insulin growth factor-1 level was lower in G2 (G1: 146.03 ng/mL vs G2: 132.25 ng/mL) (P = .369). The peak growth hormone level was also lower in G2 (G1: 4.82 ng/mL vs G2: 2.89 ng/mL) (P = .041).
Conclusion: The results showed that long COVID patients in our cohort were more likely to have anterior pituitary deficiencies. The endocrine hypothesis involving anterior pituitary insufficiency can be considered to explain long COVID.
Keywords: COVID-19; GH deficiency; SARS-CoV-2; central adrenal insufficiency; hypopituitarism; insulin tolerance test.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Long Covid: Hormone Imbalances and/or Rather Complex Immune Dysregulations?J Endocr Soc. 2024 Mar 6;8(5):bvae043. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvae043. eCollection 2024 Mar 12. J Endocr Soc. 2024. PMID: 38515584 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO . WHO COVID-19 DASHBOARD 2023 [updated 18/08/2023. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous