Retrograde Type A Acute Aortic Dissection With Cerebral Malperfusion Six Years After Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair
- PMID: 38260111
- PMCID: PMC10803006
- DOI: 10.37616/2212-5043.1363
Retrograde Type A Acute Aortic Dissection With Cerebral Malperfusion Six Years After Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair
Abstract
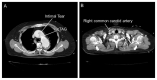
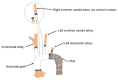
A 59-year-old male with prior thoracic endovascular aortic repair presented with altered mental status. Magnetic resonance imaging showed cerebral infarction, and subsequent computed tomography revealed acute type A aortic dissection and right carotid artery occlusion. He underwent total arch replacement with right carotid artery bypass. After successful intervention, he was transferred to a rehabilitation facility for further improvement.
Keywords: Carotid artery bypass; Retrograde type A acute aortic dissection; Thoracic endovascular aortic repair.
© 2023 Saudi Heart Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: All authors have no conflict of interest. Disclosure of funding: All authors receive no funding.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Correction of symptomatic cerebral malperfusion due to acute type I aortic dissection by transcarotid stenting of the innominate and carotid arteries.J Vasc Surg. 2006 Nov;44(5):1091-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2006.05.053. J Vasc Surg. 2006. PMID: 17098547
-
Extra-anatomic revascularization for preoperative cerebral malperfusion due to distal carotid artery occlusion in acute type A aortic dissection.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016 Feb;49(2):652-8; discussion 658-9. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezv064. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016. PMID: 25724905
-
Direct perfusion of the carotid artery in patients with brain malperfusion secondary to acute aortic dissection.Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019 Jan;67(1):161-167. doi: 10.1007/s11748-017-0873-y. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019. PMID: 29285704
-
Open retrograde endovascular stenting for left common carotid artery dissection secondary to surgical repair of acute aortic dissection: a case report and review of the literature.Ann Vasc Surg. 2015 Jul;29(5):1019.e11-5. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2015.01.017. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Ann Vasc Surg. 2015. PMID: 25765635 Review.
-
Occlusion of all aortic arch great vessels: acute revascularization to perform endovascular stroke therapy.World Neurosurg. 2014 Sep-Oct;82(3-4):535.e17-21. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2013.09.019. Epub 2013 Sep 18. World Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 24055566 Review.
References
-
- Lombardi JV, Gleason TG, Panneton JM, Starnes BW, Dake MD, Haulon S, et al. Five-year results of the STABLE II study for the endovascular treatment of complicated, acute type B aortic dissection with a composite device design J Vasc Surg 2022. 76 5 1189 1197e3 10.1016/j.jvs.2022.06.092. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Steuer J, Björck M, Sonesson B, Resch T, Dias N, Hultgren R, et al. Editor's choice – durability of endovascular repair in blunt traumatic thoracic aortic injury: long-term outcome from four tertiary referral centers Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2015. 50 4 460 5 10.1016/j.ejvs.2015.05.012. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
