Correlation of mild cognitive impairment with the thickness of retinal nerve fiber layer and serum indicators in type 2 diabetic patients
- PMID: 38260156
- PMCID: PMC10801021
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1299206
Correlation of mild cognitive impairment with the thickness of retinal nerve fiber layer and serum indicators in type 2 diabetic patients
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Correlation of mild cognitive impairment with the thickness of retinal nerve fiber layer and serum indicators in type 2 diabetic patients.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 25;15:1380375. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1380375. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38726339 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Cognitive Impairment arising from type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has garnered significant attention in recent times. However, there are few studies on the identification and diagnosis of markers of cognitive impairment. Notably, alterations in the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer's (RNFL) thickness can potentially serve as an indicative measure of central nervous system changes. Further investigations have indicated that the decline in cognitive function within T2DM patients is intricately linked to persistent systemic inflammation and the accumulation of advanced glycosylation end products. Comprehensive studies are warranted to unveil these complex associations.
Objective: This study aims to explore the potential of utilizing the RNFL thickness and serological concentrations of IL-18, irisin, CML, and RAGE as diagnostic indicators for Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) among individuals with T2DM.
Methods: The thickness of RNFL were determined in all patients and controls using optical coherence tomography (OCT). The serum levels of IL-18, irisin, CML and RAGE were detected by ELISA kit. In addition, Cognitive assessment was performed by the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) and the Montreal Cognitive assessment (MoCA).
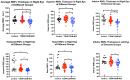
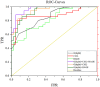
Results: The average RNFL thickness in the right eye were decreased in T2DM and T2DM combined with MCI (T2DM-MCI) patients and were positively correlated with MoCA and MMSE scores. The serum levels of IL-18, CML and RAGE in T2DM and T2DM-MCI increased significantly (p<0.05) and were negative correlated with MoCA and MMSE scores. The level of irisin in T2DM and T2DM-MCI decreased significantly (p<0.05) and were positively correlated with MoCA and MMSE scores. The area under the ROC curve of T2DM-MCI predicted by the average RNFL thickness in the right eye, CML and RAGE were 0.853, 0.874 and 0.815. The diagnostic efficacy of the combination of average RNFL thickness in the right eye, CML, and RAGE for the diagnosis of T2DM-MCI was 0.969.
Conclusion: The average RNFL thickness in the right eye, CML and RAGE have possible diagnostic value in T2DM-MCI patients.
Keywords: carboxymethyl lysine; interleukin-18; irisin; mild cognitive impairment; receptors for AGEs; the thickness of retinal nerve fiber layer; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Zheng, Xu, Lv, Mu, Zhuang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Abnormal retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and macula lutea in patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease.Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2015 Jan-Feb;60(1):162-7. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2014.10.011. Epub 2014 Oct 18. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2015. PMID: 25459918
-
The relationship between the degree of cognitive impairment and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness.Neurol Sci. 2015 Jul;36(7):1141-6. doi: 10.1007/s10072-014-2055-3. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Neurol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25575807
-
Retinal thickness as a potential biomarker of neurodegeneration and a predictor of early cognitive impairment in patients with multiple sclerosis.Neurol Res. 2020 Jul;42(7):564-574. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2020.1761174. Epub 2020 May 6. Neurol Res. 2020. PMID: 32370626
-
Optical coherence tomography in mild cognitive impairment - Systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020 Sep;196:106036. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106036. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32623211
-
Is the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) test better suited than the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) detection among people aged over 60? Meta-analysis.Psychiatr Pol. 2016 Oct 31;50(5):1039-1052. doi: 10.12740/PP/45368. Psychiatr Pol. 2016. PMID: 27992895 Review. English, Polish.
Cited by
-
Irisin: Emerging Therapeutic Targets for Cognitive Impairment-Related Diseases.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2025 Jul 15;27:e23. doi: 10.1017/erm.2025.10014. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40660735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association Between Irisin Level and Cognitive Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Brain Behav. 2025 Jul;15(7):e70662. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70662. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40696815 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

