This is a preprint.
Active site remodeling in tumor-relevant IDH1 mutants drives distinct kinetic features and potential resistance mechanisms
- PMID: 38260668
- PMCID: PMC10802581
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.01.10.574970
Active site remodeling in tumor-relevant IDH1 mutants drives distinct kinetic features and potential resistance mechanisms
Update in
-
Active site remodeling in tumor-relevant IDH1 mutants drives distinct kinetic features and potential resistance mechanisms.Nat Commun. 2024 May 6;15(1):3785. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48277-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38710674 Free PMC article.
Abstract
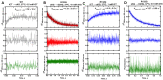
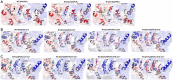
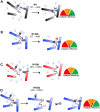
Mutations in human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) drive tumor formation in a variety of cancers by replacing its conventional activity with a neomorphic activity that generates an oncometabolite. Little is understood of the mechanistic differences among tumor-driving IDH1 mutants. We previously reported that the R132Q mutant uniquely preserves conventional activity while catalyzing robust oncometabolite production, allowing an opportunity to compare these reaction mechanisms within a single active site. Here, we employed static and dynamic structural methods and found that, compared to R132H, the R132Q active site adopted a conformation primed for catalysis with optimized substrate binding and hydride transfer to drive improved conventional and neomorphic activity over R132H. This active site remodeling revealed a possible mechanism of resistance to selective mutant IDH1 therapeutic inhibitors. This work enhances our understanding of fundamental IDH1 mechanisms while pinpointing regions for improving inhibitor selectivity.
Keywords: Enzyme mechanism; HDX-MS; IDH1; oncometabolite; structure-function relationships.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Pietrak B. et al. A tale of two subunits: how the neomorphic R132H IDH1 mutation enhances production of alphaHG. Biochemistry 50, 4804–12 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
