Clinical development of a blood biomarker using apolipoprotein-A2 isoforms for early detection of pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 38261000
- PMCID: PMC10904523
- DOI: 10.1007/s00535-023-02072-w
Clinical development of a blood biomarker using apolipoprotein-A2 isoforms for early detection of pancreatic cancer
Abstract
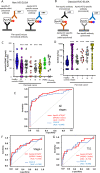
Background: We have previously reported apolipoprotein A2-isoforms (apoA2-is) as candidate plasma biomarkers for early-stage pancreatic cancer. The aim of this study was the clinical development of apoA2-is.
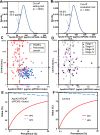
Methods: We established a new enzyme-linked immunosorbent sandwich assay for apoA2-is under the Japanese medical device Quality Management System requirements and performed in vitro diagnostic tests with prespecified end points using 2732 plasma samples. The clinical equivalence and significance of apoA2-is were compared with CA19-9.
Results: The point estimate of the area under the curve to distinguish between pancreatic cancer (n = 106) and healthy controls (n = 106) was higher for apoA2-ATQ/AT [0.879, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.832-0.925] than for CA19-9 (0.849, 95% CI 0.793-0.905) and achieved the primary end point. The cutoff apoA2-ATQ/AT of 59.5 μg/mL was defined based on a specificity of 95% in 2000 healthy samples, and the reliability of specificities was confirmed in two independent healthy cohorts as 95.3% (n = 106, 95% CI 89.4-98.0%) and 95.8% (n = 400, 95% CI 93.3-97.3%). The sensitivities of apoA2-ATQ/AT for detecting both stage I (47.4%) and I/II (50%) pancreatic cancers were higher than those of CA19-9 (36.8% and 46.7%, respectively). The combination of apoA2-ATQ/AT (cutoff, 59.5 μg/mL) and CA19-9 (37 U/mL) increased the sensitivity for pancreatic cancer to 87.7% compared with 69.8% for CA19-9 alone. The clinical performance of apoA2-is was blindly confirmed by the National Cancer Institute Early Detection Research Network.
Conclusions: The clinical performance of ApoA2-ATQ/AT as a blood biomarker is equivalent to or better than that of CA19-9.
Keywords: Apolipoprotein A2-isoform; Blood biomarker; Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9); Early detection of pancreatic cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Kazufumi Honda and Kengo Nagashima are advisers to Toray Industries, Inc. Kazufumi Honda, Giman Jung, and Michimoto Kobayashi are inventors with patent filings for apoA2-i. None of the other authors have any conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potential of Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 and Serum Apolipoprotein A2-Isoforms in the Diagnosis of Stage 0 and IA Pancreatic Cancer.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Aug 30;14(17):1920. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14171920. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272705 Free PMC article.
-
CA19-9 and apolipoprotein-A2 isoforms as detection markers for pancreatic cancer: a prospective evaluation.Int J Cancer. 2019 Apr 15;144(8):1877-1887. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31900. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30259989 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive risk stratification of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasia with malignant potential by serum apolipoprotein-A2-isoforms.Int J Cancer. 2022 Mar 1;150(5):881-894. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33875. Epub 2021 Nov 30. Int J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34778955
-
From discovery to clinical implementation of a pancreatic blood biomarker, apolipoprotein A2 isoform.Cancer Biomark. 2025 Mar;42(3):18758592251317405. doi: 10.1177/18758592251317405. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Cancer Biomark. 2025. PMID: 40171807 Review.
-
Potential usefulness of apolipoprotein A2 isoforms for screening and risk stratification of pancreatic cancer.Biomark Med. 2016 Nov;10(11):1197-1207. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2016-0209. Epub 2016 Sep 27. Biomark Med. 2016. PMID: 27673558 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of immune infiltration-related ZNF480 for predicting prognosis in breast cancer.Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2025 Feb 25;14(1):1-13. doi: 10.62347/LNKO2367. eCollection 2025. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40134826 Free PMC article.
-
Early-Stage Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis: Serum Biomarkers and the Potential for Aptamer-Based Biosensors.Molecules. 2025 Apr 30;30(9):2012. doi: 10.3390/molecules30092012. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40363817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of novel biomarkers in the early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2025 May 23;20(5):e0322720. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322720. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40408437 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles for Clinical Diagnostics: From Bulk Measurements to Single-Vesicle Analysis.ACS Nano. 2025 Aug 12;19(31):28021-28109. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5c00706. Epub 2025 Jul 28. ACS Nano. 2025. PMID: 40720603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 and Serum Apolipoprotein A2-Isoforms in the Diagnosis of Stage 0 and IA Pancreatic Cancer.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Aug 30;14(17):1920. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14171920. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272705 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

