Functional analysis of chromatin-associated proteins in Sordaria macrospora reveals similar roles for RTT109 and ASF1 in development and DNA damage response
- PMID: 38261383
- PMCID: PMC10917505
- DOI: 10.1093/g3journal/jkae019
Functional analysis of chromatin-associated proteins in Sordaria macrospora reveals similar roles for RTT109 and ASF1 in development and DNA damage response
Abstract
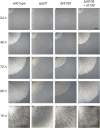
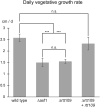
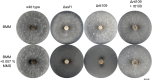
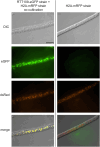
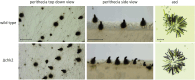
We performed a functional analysis of two potential partners of ASF1, a highly conserved histone chaperone that plays a crucial role in the sexual development and DNA damage resistance in the ascomycete Sordaria macrospora. ASF1 is known to be involved in nucleosome assembly and disassembly, binding histones H3 and H4 during transcription, replication and DNA repair and has direct and indirect roles in histone recycling and modification as well as DNA methylation, acting as a chromatin modifier hub for a large network of chromatin-associated proteins. Here, we functionally characterized two of these proteins, RTT109 and CHK2. RTT109 is a fungal-specific histone acetyltransferase, while CHK2 is an ortholog to PRD-4, a checkpoint kinase of Neurospora crassa that performs similar cell cycle checkpoint functions as yeast RAD53. Through the generation and characterization of deletion mutants, we discovered striking similarities between RTT109 and ASF1 in terms of their contributions to sexual development, histone acetylation, and protection against DNA damage. Phenotypic observations revealed a developmental arrest at the same stage in Δrtt109 and Δasf1 strains, accompanied by a loss of H3K56 acetylation, as detected by western blot analysis. Deletion mutants of rtt109 and asf1 are sensitive to the DNA damaging agent methyl methanesulfonate, but not hydroxyurea. In contrast, chk2 mutants are fertile and resistant to methyl methanesulfonate, but not hydroxyurea. Our findings suggest a close functional association between ASF1 and RTT109 in the context of development, histone modification, and DNA damage response, while indicating a role for CHK2 in separate pathways of the DNA damage response.
Keywords: Sordaria macrospora; asf1; chk2; rtt109; DNA damage response; chromatin-associated proteins; fruiting body development; functional genomics.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Genetics Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Promoter regulation by distinct mechanisms of functional interplay between lysine acetylase Rtt109 and histone chaperone Asf1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Dec 6;108(49):19599-604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111501108. Epub 2011 Nov 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 22106264 Free PMC article.
-
Two factor authentication: Asf1 mediates crosstalk between H3 K14 and K56 acetylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Aug 22;47(14):7380-7391. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz508. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31194870 Free PMC article.
-
Chaperone control of the activity and specificity of the histone H3 acetyltransferase Rtt109.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jul;28(13):4342-53. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00182-08. Epub 2008 May 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18458063 Free PMC article.
-
The histone chaperone Asf1 at the crossroads of chromatin and DNA checkpoint pathways.Chromosoma. 2007 Apr;116(2):79-93. doi: 10.1007/s00412-006-0087-z. Epub 2006 Dec 19. Chromosoma. 2007. PMID: 17180700 Review.
-
Understanding histone acetyltransferase Rtt109 structure and function: how many chaperones does it take?Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2011 Dec;21(6):728-34. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2011.09.005. Epub 2011 Oct 23. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2011. PMID: 22023828 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
