Tracking the role of Aire in immune tolerance to the eye with a TCR transgenic mouse model
- PMID: 38261611
- PMCID: PMC10835137
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2311487121
Tracking the role of Aire in immune tolerance to the eye with a TCR transgenic mouse model
Abstract
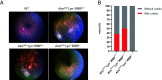
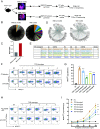
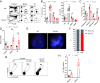
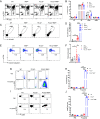
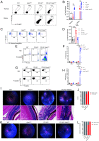
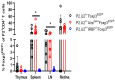
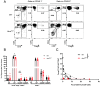
Roughly one-half of mice with partial defects in two immune tolerance pathways (AireGW/+Lyn-/- mice) spontaneously develop severe damage to their retinas due to T cell reactivity to Aire-regulated interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP). Single-cell T cell receptor (TCR) sequencing of CD4+ T cells specific for a predominate epitope of IRBP showed a remarkable diversity of autoantigen-specific TCRs with greater clonal expansions in mice with disease. TCR transgenic mice made with an expanded IRBP-specific TCR (P2.U2) of intermediate affinity exhibited strong but incomplete negative selection of thymocytes. This negative selection was absent in IRBP-/- mice and greatly defective in AireGW/+ mice. Most P2.U2+/- mice and all P2.U.2+/-AireGW/+ mice rapidly developed inflammation of the retina and adjacent uvea (uveitis). Aire-dependent IRBP expression in the thymus also promoted Treg differentiation, but the niche for this fate determination was small, suggesting differences in antigen presentation leading to negative selection vs. thymic Treg differentiation and a stronger role for negative selection in preventing autoimmune disease in the retina.
Keywords: Aire; IRBP; autoimmune; negative selection; uveitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Goodnow C. C., Multistep pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Cell 130, 25–35 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Cho J. H., Gregersen P. K., Genomics and the multifactorial nature of human autoimmune disease. N Engl. J. Med. 365, 1612–1623 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Hori S., Nomura T., Sakaguchi S., Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 299, 1057–1061 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Khattri R., Cox T., Yasayko S. A., Ramsdell F., An essential role for Scurfin in CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells. Nat. Immunol. 4, 337–342 (2003). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

