Engineering peroxisomal biosynthetic pathways for maximization of triterpene production in Yarrowia lipolytica
- PMID: 38261612
- PMCID: PMC10835042
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2314798121
Engineering peroxisomal biosynthetic pathways for maximization of triterpene production in Yarrowia lipolytica
Abstract
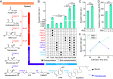
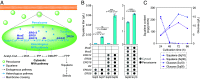
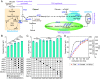
Constructing efficient cell factories for product synthesis is frequently hampered by competing pathways and/or insufficient precursor supply. This is particularly evident in the case of triterpenoid biosynthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica, where squalene biosynthesis is tightly coupled to cytosolic biosynthesis of sterols essential for cell viability. Here, we addressed this problem by reconstructing the complete squalene biosynthetic pathway, starting from acetyl-CoA, in the peroxisome, thus harnessing peroxisomal acetyl-CoA pool and sequestering squalene synthesis in this organelle from competing cytosolic reactions. This strategy led to increasing the squalene levels by 1,300-fold relatively to native cytosolic synthesis. Subsequent enhancement of the peroxisomal acetyl-CoA supply by two independent approaches, 1) converting cellular lipid pool to peroxisomal acetyl-CoA and 2) establishing an orthogonal acetyl-CoA shortcut from CO2-derived acetate in the peroxisome, further significantly improved local squalene accumulation. Using these approaches, we constructed squalene-producing strains capable of yielding 32.8 g/L from glucose, and 31.6 g/L from acetate by employing a cofeeding strategy, in bioreactor fermentations. Our findings provide a feasible strategy for protecting intermediate metabolites that can be claimed by multiple reactions by engineering peroxisomes in Y. lipolytica as microfactories for the production of such intermediates and in particular acetyl-CoA-derived metabolites.
Keywords: acetate metabolism; metabolic engineering; orthogonal pathway; peroxisome; triterpenoids.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:Y.M. and G.S. are coinventors in a patent application (Serial No.: 63/481,957) describing the squalene production using the strategies reported here.
Figures

References
-
- Chen Y., Nielsen J., Advances in metabolic pathway and strain engineering paving the way for sustainable production of chemical building blocks. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 24, 965–972 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Peralta-Yahya P. P., Zhang F., Del Cardayre S. B., Keasling J. D., Microbial engineering for the production of advanced biofuels. Nature 488, 320–328 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Liu Y., Nielsen J., Recent trends in metabolic engineering of microbial chemical factories. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 60, 188–197 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Vickers C. E., Williams T. C., Peng B., Cherry J., Recent advances in synthetic biology for engineering isoprenoid production in yeast. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 40, 47–56 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Nielsen J., Keasling J. D., Engineering cellular metabolism. Cell 164, 1185–1197 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

