Activation of Notch-1 signaling pathway in macrophages to secrete PD-L1 and regulate cytotoxicity of CAR-T cells in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 38261741
- PMCID: PMC10866421
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205463
Activation of Notch-1 signaling pathway in macrophages to secrete PD-L1 and regulate cytotoxicity of CAR-T cells in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the mechanism of action of the Notch-1/IRE1/XBP1s signaling pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
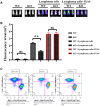
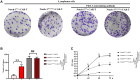
Methods: The expressions of relevant proteins were detected by Western blotting. The effect of myeloid-specific knockout of Notch-1 on lymphoma progression was observed by mouse tumor transplantation and imaging. The apoptosis of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy (CAR-T) cells were detected by flow cytometry, and the proliferation of CAR-T cells was detected by wound healing assay and cell counting kit-8 (CCK8) assay.
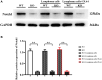
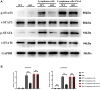
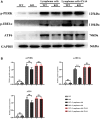
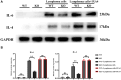
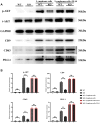
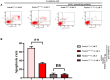
Results: Lymphoma cells mediated the Notch-1 signaling pathway in bone marrow-derived macrophages and promoted the activation of STAT3 and STAT6 in bone marrow-derived macrophages. Myeloid-specific knockout of Notch-1 could inhibit the progression of lymphoma. Lymphoma cells enhanced the expression of p-PERK, p-IRE1α, ATF6, IL-6, IL-4, p-AKT, CD9, CD63 and PD-L1 in bone marrow-derived macrophages by mediating the Notch-1 signaling pathway. Knockout of Notch-1 in macrophages alleviated, to some extent, the suppression of killing activity of CAR-T cells, while activation of Notch-1 in macrophages inhibited proliferation and promoted apoptosis of CAR-T cells. The PD-L1 antibody significantly restored the cytotoxicity and proliferation of CAR-T cells, and inhibited their apoptosis.
Conclusion: Activation of the Notch-1/IRE1/XBP1s signaling pathway in myeloid macrophages promotes the secretion of IL-6 and IL-4 as well as PD-L1, thereby inhibiting the activity and proliferation of CAR-T cells and promoting their apoptosis.
Keywords: CAR-T cells; Notch-1/IRE1/XBP1s signaling pathway; PD-L1; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
CD19-specific CAR T Cells that Express a PD-1/CD28 Chimeric Switch-Receptor are Effective in Patients with PD-L1-positive B-Cell Lymphoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Jan 15;27(2):473-484. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-1457. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33028589 Clinical Trial.
-
LncRNA MALAT1 promotes tumorigenesis and immune escape of diffuse large B cell lymphoma by sponging miR-195.Life Sci. 2019 Aug 15;231:116335. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.03.040. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30898647
-
ILT4 inhibition prevents TAM- and dysfunctional T cell-mediated immunosuppression and enhances the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy in NSCLC with EGFR activation.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 19;11(7):3392-3416. doi: 10.7150/thno.52435. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33537094 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of PD-1/PD-L1 expression in the tumor microenvironment and neoplastic cells for lymphoma.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Dec;77:105999. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105999. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31704289 Review.
-
PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway and Its Blockade in Patients with Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin Large-Cell Lymphomas.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2020 Aug;15(4):372-381. doi: 10.1007/s11899-020-00589-y. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2020. PMID: 32394185 Review.
Cited by
-
ATF6 activation promotes tumorigenesis and drug resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) by regulating the mTOR/S6K signaling pathway.Discov Oncol. 2025 Apr 9;16(1):499. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02264-1. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40205285 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-a key guardian in cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Jul 30;10(1):343. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02110-3. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39080273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Biology Hides Novel Therapeutic Approaches to Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 23;25(21):11384. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111384. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39518937 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chapuy B, Stewart C, Dunford AJ, Kim J, Kamburov A, Redd RA, Lawrence MS, Roemer MGM, Li AJ, Ziepert M, Staiger AM, Wala JA, Ducar MD, et al.. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat Med. 2018; 24:679–90. 10.1038/s41591-018-0016-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Neelapu SS, Locke FL, Bartlett NL, Lekakis LJ, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, Braunschweig I, Oluwole OO, Siddiqi T, Lin Y, Timmerman JM, Stiff PJ, Friedberg JW, et al.. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:2531–44. 10.1056/NEJMoa1707447 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

