Activation of Notch-1 signaling pathway in macrophages to secrete PD-L1 and regulate cytotoxicity of CAR-T cells in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 38261741
- PMCID: PMC10866421
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205463
Activation of Notch-1 signaling pathway in macrophages to secrete PD-L1 and regulate cytotoxicity of CAR-T cells in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the mechanism of action of the Notch-1/IRE1/XBP1s signaling pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
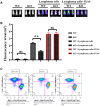
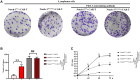
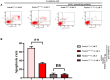
Methods: The expressions of relevant proteins were detected by Western blotting. The effect of myeloid-specific knockout of Notch-1 on lymphoma progression was observed by mouse tumor transplantation and imaging. The apoptosis of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy (CAR-T) cells were detected by flow cytometry, and the proliferation of CAR-T cells was detected by wound healing assay and cell counting kit-8 (CCK8) assay.
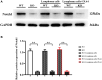
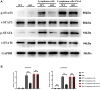
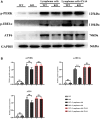
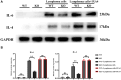
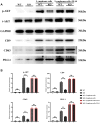
Results: Lymphoma cells mediated the Notch-1 signaling pathway in bone marrow-derived macrophages and promoted the activation of STAT3 and STAT6 in bone marrow-derived macrophages. Myeloid-specific knockout of Notch-1 could inhibit the progression of lymphoma. Lymphoma cells enhanced the expression of p-PERK, p-IRE1α, ATF6, IL-6, IL-4, p-AKT, CD9, CD63 and PD-L1 in bone marrow-derived macrophages by mediating the Notch-1 signaling pathway. Knockout of Notch-1 in macrophages alleviated, to some extent, the suppression of killing activity of CAR-T cells, while activation of Notch-1 in macrophages inhibited proliferation and promoted apoptosis of CAR-T cells. The PD-L1 antibody significantly restored the cytotoxicity and proliferation of CAR-T cells, and inhibited their apoptosis.
Conclusion: Activation of the Notch-1/IRE1/XBP1s signaling pathway in myeloid macrophages promotes the secretion of IL-6 and IL-4 as well as PD-L1, thereby inhibiting the activity and proliferation of CAR-T cells and promoting their apoptosis.
Keywords: CAR-T cells; Notch-1/IRE1/XBP1s signaling pathway; PD-L1; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Chapuy B, Stewart C, Dunford AJ, Kim J, Kamburov A, Redd RA, Lawrence MS, Roemer MGM, Li AJ, Ziepert M, Staiger AM, Wala JA, Ducar MD, et al.. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat Med. 2018; 24:679–90. 10.1038/s41591-018-0016-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Neelapu SS, Locke FL, Bartlett NL, Lekakis LJ, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, Braunschweig I, Oluwole OO, Siddiqi T, Lin Y, Timmerman JM, Stiff PJ, Friedberg JW, et al.. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:2531–44. 10.1056/NEJMoa1707447 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

