IL-17 promotes IL-18 production via the MEK/ERK/miR-4492 axis in osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts
- PMID: 38261743
- PMCID: PMC10866453
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205462
IL-17 promotes IL-18 production via the MEK/ERK/miR-4492 axis in osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts
Abstract
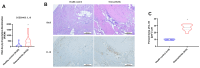
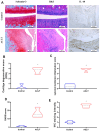
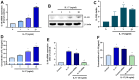
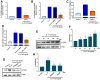
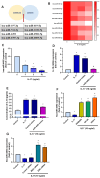
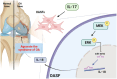
The concept of osteoarthritis (OA) as a low-grade inflammatory joint disorder has been widely accepted. Many inflammatory mediators are implicated in the pathogenesis of OA. Interleukin (IL)-18 is a pleiotropic cytokine with versatile cellular functions that are pathogenetically important in immune responses, as well as autoimmune, inflammatory, and infectious diseases. IL-17, a proinflammatory cytokine mainly secreted by Th17 cells, is upregulated in OA patients. However, the role of IL-17 in OA progression is unclear. The synovial tissues collected from healthy donors and OA patients were used to detect the expression level of IL-18 by IHC stain. The OA synovial fibroblasts (OASFs) were incubated with recombinant IL-17 and subjected to Western blot, qPCR, and ELISA to examine IL-18 expression level. The chemical inhibitors and siRNAs which targeted signal pathways were used to investigate signal pathways involved in IL-17-induced IL-18 expression. The microRNAs which participated IL-18 expression were surveyed with online databases miRWalk and miRDB, followed by validation with qPCR. This study revealed significantly higher levels of IL-18 expression in synovial tissue from OA patients compared with healthy controls, as well as increased IL-18 expression in OASFs from rats with severe OA. In vitro findings indicated that IL-17 dose-dependently promoted IL-18 production in OASFs. Molecular investigations revealed that the MEK/ERK/miR-4492 axis stimulated IL-18 production when OASFs were treated with IL-17. This study provides novel insights into the role of IL-17 in the pathogenesis of OA, which may help to inform OA treatment in the future.
Keywords: IL-17; IL-18; osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Resistin enhances IL-1β and TNF-α expression in human osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts by inhibiting miR-149 expression via the MEK and ERK pathways.FASEB J. 2020 Oct;34(10):13671-13684. doi: 10.1096/fj.202001071R. Epub 2020 Aug 13. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32790946
-
Visfatin Promotes IL-6 and TNF-α Production in Human Synovial Fibroblasts by Repressing miR-199a-5p through ERK, p38 and JNK Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 8;19(1):190. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010190. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29316707 Free PMC article.
-
CCN2 Facilitates IL-17 Production and Osteoclastogenesis in Human Osteoarthritis Synovial Fibroblasts by Inhibiting miR-655 Expression.J Bone Miner Res. 2022 Oct;37(10):1944-1955. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4661. Epub 2022 Aug 8. J Bone Miner Res. 2022. PMID: 35876037
-
Nesfatin-1 facilitates IL-1β production in osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts by suppressing miR-204-5p synthesis through the AP-1 and NF-κB pathways.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Sep 24;13(18):22490-22501. doi: 10.18632/aging.203559. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34560673 Free PMC article.
-
Forkhead box C1 promotes the pathology of osteoarthritis by upregulating β-catenin in synovial fibroblasts.FEBS J. 2020 Jul;287(14):3065-3087. doi: 10.1111/febs.15178. Epub 2019 Dec 29. FEBS J. 2020. PMID: 31837247
Cited by
-
Regulation of ferroptosis in osteoarthritis and osteoarthritic chondrocytes by typical MicroRNAs in chondrocytes.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 5;11:1478153. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1478153. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39564502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

