GRK2 inhibits Flt-1+ macrophage infiltration and its proangiogenic properties in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 38261818
- PMCID: PMC10792976
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.09.013
GRK2 inhibits Flt-1+ macrophage infiltration and its proangiogenic properties in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
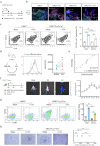
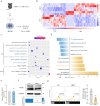
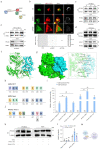
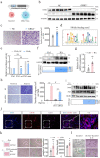
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease with a complex etiology. Monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs) infiltration are associated with RA severity. We have reported the deletion of G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) reprograms macrophages toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype by recovering G-protein-coupled receptor signaling. However, as more GRK2-interacting proteins were discovered, the GRK2 interactome mechanisms in RA have been understudied. Thus, in the collagen-induced arthritis mouse model, we performed genetic GRK2 deletion using GRK2f/fLyz2-Cre+/- mice. Synovial inflammation and M1 polarization were improved in GRK2f/fLyz2-Cre+/- mice. Supporting experiments with RNA-seq and dual-luciferase reporter assays identified peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) as a new GRK2-interacting protein. We further confirmed that fms-related tyrosine kinase 1 (Flt-1), which promoted macrophage migration to induce angiogenesis, was inhibited by GRK2-PPARγ signaling. Mechanistically, excess GRK2 membrane recruitment in CIA MDMs reduced the activation of PPARγ ligand-binding domain and enhanced Flt-1 transcription. Furthermore, the treatment of mice with GRK2 activity inhibitor resulted in significantly diminished CIA pathology, Flt-1+ macrophages induced-synovial inflammation, and angiogenesis. Altogether, we anticipate to facilitate the elucidation of previously unappreciated details of GRK2-specific intracellular signaling. Targeting GRK2 activity is a viable strategy to inhibit MDMs infiltration, affording a distinct way to control joint inflammation and angiogenesis of RA.
Keywords: Flt-1; GRK2; Monocyte-derived macrophages; PPARγ; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The intersection of GRK2 and PGE2 in rheumatoid arthritis: a comprehensive update on pathophysiology and treatment.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 22. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04163-2. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40261352 Review.
-
GRK2 Mediated Abnormal Transduction of PGE2-EP4-cAMP-CREB Signaling Induces the Imbalance of Macrophages Polarization in Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mice.Cells. 2019 Dec 8;8(12):1596. doi: 10.3390/cells8121596. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31818003 Free PMC article.
-
GRK2-mediated phosphorylation and de-succinylation of PKM2 reduce macrophage glycolysis in rheumatoid arthritis.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 May 27. doi: 10.1038/s41401-025-01582-y. Online ahead of print. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 40425786
-
Wutou decoction attenuates the synovial inflammation of collagen-induced arthritis rats via regulating macrophage M1/M2 type polarization.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jan 30;301:115802. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115802. Epub 2022 Oct 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36209953
-
Targeted inhibition of the GRK2/HIF-1α pathway is an effective strategy to alleviate synovial hypoxia and inflammation.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Dec;113(Pt A):109271. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109271. Epub 2022 Nov 10. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36461590 Review.
Cited by
-
Optineurin restrains CCR7 degradation to guide type II collagen-stimulated dendritic cell migration in rheumatoid arthritis.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025 Mar;15(3):1626-1642. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2025.02.004. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025. PMID: 40370566 Free PMC article.
-
The intersection of GRK2 and PGE2 in rheumatoid arthritis: a comprehensive update on pathophysiology and treatment.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 22. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04163-2. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40261352 Review.
-
GRK2 activates TRAF2-NF-κB signalling to promote hyperproliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025 Apr;15(4):1956-1973. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2025.02.031. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025. PMID: 40486864 Free PMC article.
-
A Matrigel-Free 3D Chondrocytic Spheroid Model for Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Synoviocytes Invasion Studies.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Mar 24;18:4319-4334. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S504701. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40162078 Free PMC article.
-
MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms and therapeutic potential.PeerJ. 2025 Jul 14;13:e19708. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19708. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40677749 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Safiri S., Kolahi A.A., Hoy D., Smith E., Bettampadi D., Mansournia M.A., et al. Regional and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis 1990‒2017: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:1463–1471. - PubMed
-
- Udalova I.A., Mantovani A., Feldmann M. Macrophage heterogeneity in the context of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12:472–485. - PubMed
-
- Alivernini S., MacDonald L., Elmesmari A., Finlay S., Tolusso B., Gigante M.R., et al. Distinct synovial tissue macrophage subsets regulate inflammation and remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med. 2020;26:1295–1306. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

