5-Hydroxymethylcytosine signals in serum are a predictor of chemoresistance in high-grade serous ovarian cancer
- PMID: 38262243
- PMCID: PMC11246748
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2024.01.001
5-Hydroxymethylcytosine signals in serum are a predictor of chemoresistance in high-grade serous ovarian cancer
Abstract
Objective: The genome-wide profiling of 5-hydroxymethylcytosines (5hmC) on circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has revealed promising biomarkers for various diseases. The purpose of this study was to investigate 5hmC signals in serum cfDNA and identify novel predictive biomarkers for the development of chemoresistance in high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC). We hypothesized that 5hmC profiles in cfDNA reflect the development of chemoresistance and elucidate pathways that may drive chemoresistance in HGSOC. Moreover, we sought to identify predictors that would better stratify outcomes for women with intermediate-sensitive HGSOC.
Methods: Women diagnosed with HGSOC and known platinum sensitivity status were selected for this study. Nano-hmC-Seal was performed on cfDNA isolated from archived serum samples, and differential 5hmC features were identified using DESeq2 to establish a model predictive of chemoresistance.
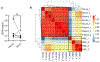
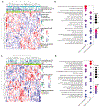
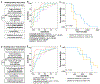
Results: A multivariate model consisting of three features (preoperative CA-125, largest residual implant after surgery, 5hmC level of OSGEPL), stratified samples from intermediate sensitive, chemo-naive women diagnosed with HGSOC into chemotherapy-resistant- and sensitive-like strata with a significant difference in overall survival (OS). Independent analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas data further confirmed that high OSGEPL1 expression is a favorable prognostic factor for HGSOC.
Conclusions: We have developed a novel multivariate model based on clinico-pathologic data and a cfDNA-derived 5hmC modified gene, OSGEPL1, that predicted response to platinum-based chemotherapy in intermediate-sensitive HGSOC. Our multivariate model applies to chemo-naïve samples regardless if the patint was treated with adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy. These results merit further investigation of the predictive capability of our model in larger cohorts.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Cell-free DNA, liquid biopsies; Chemotherapy resistance; High-grade serous ovarian cancer.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Ernst Lengyel reported receiving research funding to perform experimental pre-clinical research on ovarian cancer from Arsenal Bioscience, AbbVie, outside the submitted work. Chuan He is a scientific founder, a member of the scientific advisory board and equity holder of Aferna Bio, Inc., and AccuraDX Inc., a scientific cofounder and equity holder of Accent Therapeutics, Inc., and a member of the scientific advisory board of Rona Therapeutics. Wei Zhang is a consultant for the biomarker discovery program of Tempus Labs, Inc. All other authors declare no relationships that may present a conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Markmann M, et al. , Second-line platinum therapy in patients with ovarian cancer previously treated with cisplatin, J. Clin. Oncol 9 (3) (1991) 389–393. - PubMed
-
- Gore ME, et al. , Treatment of relapsed carcinoma of the ovary with cisplatin or carboplatin following initial treatment with these compounds, Gynecol. Oncol 36 (2) (1990) 207–211. - PubMed
-
- Nishiyama A, Nakanishi M, Navigating the DNA methylation landscape of cancer, Trends Genet. 37 (11) (2021) 1012–1027. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

