Cold-induced changes in plasma signaling lipids are associated with a healthier cardiometabolic profile independently of brown adipose tissue
- PMID: 38262411
- PMCID: PMC10897514
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101387
Cold-induced changes in plasma signaling lipids are associated with a healthier cardiometabolic profile independently of brown adipose tissue
Abstract
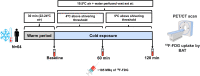
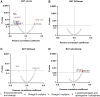
Cold exposure activates brown adipose tissue (BAT) and potentially improves cardiometabolic health through the secretion of signaling lipids by BAT. Here, we show that 2 h of cold exposure in young adults increases the levels of omega-6 and omega-3 oxylipins, the endocannabinoids (eCBs) anandamide and docosahexaenoylethanolamine, and lysophospholipids containing polyunsaturated fatty acids. Contrarily, it decreases the levels of the eCBs 1-LG and 2-LG and 1-OG and 2-OG, lysophosphatidic acids, and lysophosphatidylethanolamines. Participants overweight or obese show smaller increases in omega-6 and omega-3 oxylipins levels compared to normal weight. We observe that only a small proportion (∼4% on average) of the cold-induced changes in the plasma signaling lipids are slightly correlated with BAT volume. However, cold-induced changes in omega-6 and omega-3 oxylipins are negatively correlated with adiposity, glucose homeostasis, lipid profile, and liver parameters. Lastly, a 24-week exercise-based randomized controlled trial does not modify plasma signaling lipid response to cold exposure.
Keywords: adiposity; bioactive lipids; brown adipose tissue; cardiometabolic health; cold; endocannabinoids; lipidomics; obesity; oxylipins; polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Vedanthan R., Fuster V. Urgent need for human resources to promote global cardiovascular health. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2011;8:114–117. Preprint. - PubMed
-
- Organization, W.H. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs).
-
- WHO . 2018. Noncommunicable Diseases Country Profiles 2018.
-
- Blüher M. Preprint at Nature Publishing Group; 2019. Obesity: Global Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. - PubMed
-
- Ruiz J.R., Martinez-Tellez B., Sanchez-Delgado G., Osuna-Prieto F.J., Rensen P.C.N., Boon M.R. Role of Human Brown Fat in Obesity, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Disease: Strategies to Turn Up the Heat. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018;61:232–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

