Integrative genomic analyses reveal putative cell type-specific targets of the Drosophila ets transcription factor Pointed
- PMID: 38262913
- PMCID: PMC10807358
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-024-10017-7
Integrative genomic analyses reveal putative cell type-specific targets of the Drosophila ets transcription factor Pointed
Abstract
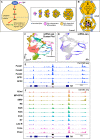
The Ets domain transcription factors direct diverse biological processes throughout all metazoans and are implicated in development as well as in tumor initiation, progression and metastasis. The Drosophila Ets transcription factor Pointed (Pnt) is the downstream effector of the Epidermal growth factor receptor (Egfr) pathway and is required for cell cycle progression, specification, and differentiation of most cell types in the larval eye disc. Despite its critical role in development, very few targets of Pnt have been reported previously. Here, we employed an integrated approach by combining genome-wide single cell and bulk data to identify putative cell type-specific Pnt targets. First, we used chromatin immunoprecipitation with high-throughput sequencing (ChIP-seq) to determine the genome-wide occupancy of Pnt in late larval eye discs. We identified enriched regions that mapped to an average of 6,941 genes, the vast majority of which are novel putative Pnt targets. Next, we integrated ChIP-seq data with two other larval eye single cell genomics datasets (scRNA-seq and snATAC-seq) to reveal 157 putative cell type-specific Pnt targets that may help mediate unique cell type responses upon Egfr-induced differentiation. Finally, our integrated data also predicts cell type-specific functional enhancers that were not reported previously. Together, our study provides a greatly expanded list of putative cell type-specific Pnt targets in the eye and is a resource for future studies that will allow mechanistic insights into complex developmental processes regulated by Egfr signaling.
Keywords: Differentiation; Drosophila eye disc; Epidermal growth factor receptor; Integrative genomics; Pointed-ChIP-seq; Single cell genomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
GM is co-owner of Genetivision Corporation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
EGFR/Ras Signaling Controls Drosophila Intestinal Stem Cell Proliferation via Capicua-Regulated Genes.PLoS Genet. 2015 Dec 18;11(12):e1005634. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005634. eCollection 2015 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26683696 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study of Pointed and Yan expression reveals new complexity to the transcriptional networks downstream of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling.Dev Biol. 2014 Jan 15;385(2):263-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24240101 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential activation of ETS proteins provides a sustained transcriptional response to EGFR signaling.Development. 2013 Jul;140(13):2746-54. doi: 10.1242/dev.093138. Development. 2013. PMID: 23757412
-
Lessons from Drosophila Pointed, an ETS family transcription factor and key nuclear effector of the RTK signaling pathway.Genesis. 2018 Dec;56(11-12):e23257. doi: 10.1002/dvg.23257. Epub 2018 Nov 25. Genesis. 2018. PMID: 30318758 Review.
-
Sequence and functional properties of Ets genes in the model organism Drosophila.Oncogene. 2000 Dec 18;19(55):6409-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204033. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11175357 Review.
Cited by
-
A single cell RNA sequence atlas of the early Drosophila larval eye.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jun 19;25(1):616. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10423-x. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38890587 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

