Pooling sputum samples for the Xpert MTB/RIF assay: a practical screening strategy for highly infectious tuberculosis cases
- PMID: 38262989
- PMCID: PMC10807086
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-024-09020-w
Pooling sputum samples for the Xpert MTB/RIF assay: a practical screening strategy for highly infectious tuberculosis cases
Abstract
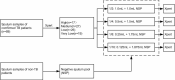
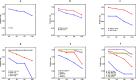
The Xpert MTB/RIF test (Xpert) can help in the accurate screening of tuberculosis, however, its widespread use is limited by its high cost and lack of accessibility. Pooling of sputum samples for testing is a strategy to cut expenses and enhance population coverage but may result in a decrease in detection sensitivity due to the dilution of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) by sample mixing. We investigated how the mixing ratio affected the detection performance of Xpert. We used frozen sputum samples that had been kept after individual Xpert assays of the sputa from Mtb-confirmed TB patients and non-TB patients. Our results showed that the overall sensitivity of the Xpert pooling assay remained higher than 80% when the mixing ratio was between 1/2 and 1/8. When the mixing ratio was raised to 1/16, the positive detection rate fell to 69.0%. For patients with either a high sputum Mtb smear score ≥ 2+, a time-to-positive culture ≤ 10 days, or an Xpert test indicating a high or medium abundance of bacteria, the pooling assay positivity rates were 93.3%, 96.8%, and 100% respectively, even at a 1/16 mixing ratio. For participants with cavities and cough, the pooling assay positivity rates were 86.2% and 90.0% at a 1/8 ratio, higher than for those without these signs. Our results show that the Xpert pooled assay has a high overall sensitivity, especially for highly infectious patients. This pooling strategy with lower reagent and labor costs could support TB screening in communities with limited resources, thereby facilitating reductions in the community transmission and incidence of TB worldwide.
Keywords: Active screening; Infectivity; Pooling assay; Tuberculosis; Xpert.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid and accurate detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum samples by Cepheid Xpert MTB/RIF assay--a clinical validation study.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020458. Epub 2011 Jun 29. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21738575 Free PMC article.
-
The New Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra: Improving Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Resistance to Rifampin in an Assay Suitable for Point-of-Care Testing.mBio. 2017 Aug 29;8(4):e00812-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00812-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28851844 Free PMC article.
-
Pooling sputum samples for the Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra assay: A sensitive and effective screening strategy.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2024 Dec;149:102575. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2024.102575. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2024. PMID: 39541856
-
Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert Ultra assays for screening for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults, irrespective of signs or symptoms.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 23;3(3):CD013694. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013694.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33755189 Free PMC article.
-
Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra assays for active tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 27;8(8):CD013359. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013359.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 6;9:CD013359. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013359.pub3. PMID: 32853411 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Xpert MTB/RIF assay in detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis in samples with different results by smear and culture in a coastal city with high incidence of tuberculosis.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Jan 11;25(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10446-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39799307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . Global tuberculosis report 2022. Geneva: World Health Organization. In; 2022.
-
- WHO . Global tuberculosis report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization. In; 2021.
-
- WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee. In: WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis: Module 2: screening– systematic screening for tuberculosis disease. edn. Geneva: World Health Organization© World Health Organization 2021.; 2021.
-
- Lawn SD, Mwaba P, Bates M, Piatek A, Alexander H, Marais BJ, Cuevas LE, McHugh TD, Zijenah L, Kapata N, et al. Advances in Tuberculosis diagnostics: the Xpert MTB/RIF assay and future prospects for a point-of-care test. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13(4):349–61. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70008-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdurrahman ST, Mbanaso O, Lawson L, Oladimeji O, Blakiston M, Obasanya J, Dacombe R, Adams ER, Emenyonu N, Sahu S, et al. Testing pooled sputum with Xpert MTB/RIF for diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis to increase affordability in low-income countries. J Clin Microbiol. 2015;53(8):2502–8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00864-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2020B1111170014/the Special Fund for Science and Technology Innovation of Guangdong
- SZGSPO10/the Shenzhen Fund for Guangdong Provincial High-level Clinical Key Specialties
- JCYJ20220530163212027/Shenzhen Natural Science Foundation
- 20210617141509001/the Shenzhen Clinical Research Center for Tuberculosis
- LCYX20220620105200001/the Special Fund Of Shenzhen Central-leading-local Scientific and Technological Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

