Moderating role of 1-minute abdominal test in the relationship between cardiometabolic risk factors and adiponectin concentration in adolescents
- PMID: 38263075
- PMCID: PMC10804517
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-024-04554-z
Moderating role of 1-minute abdominal test in the relationship between cardiometabolic risk factors and adiponectin concentration in adolescents
Abstract
Background: Adiponectin is an anti-inflammatory cytokine secreted by adipose tissue, has been associated with adiposity and cardiometabolic risk, and has controversial results with muscular fitness. The aim of this study was to analyze the interaction of 1-minute abdominal test in the relationship between adiposity, body composition, cardiometabolic risk and adiponectin concentration in adolescents.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study conducted with 62 adolescents of both sexes, aged 11 to 16 years, approved by the Ethics Committee of Research in Humans (CAEE: 62963916.0.0000.5223). Body mass, height, abdominal circumference (AC), waist circumference (WC), fat mass (FM), fat-free mass (FFM), high density lipoprotein (HDL-c), low density lipoprotein (LDL-c), triglycerides (TG), adiponectin, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and mean blood pressure (MBP), 1-minute abdominal test (ABD) were measured. Body mass index (BMI), z-score BMI (BMI-z), triponderal mass index (TMI), and waist-to-height ratio (WHtR) were calculated. The macro PROCESS for SPSS v.24.0 was used for moderation analyses, with linear regression models.
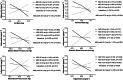
Results: Inverse interactions were found for adiposity (BMI, BMI-z, TMI, AC, WC, WHtR), body composition (FM, FFM) and CMRF (SBP, DBP, MBP, TG) versus 1-minute abdominal test with adiponectin concentration, demonstrating that abdominal test is a moderator in these relationships.
Conclusion: We conclude that 1-minute abdominal test may play an important role in the relationship between obesity and cardiometabolic risk. We found that muscular fitness can confer a protective effect on adolescents with high levels of abdominal test.
Keywords: Adipokines; Adiposity; Muscular fitness; Physical fitness; Risk factors; Youth.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests and they do not have professional relationships with companies that will benefit from the results of this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lower adiponectin is associated with higher anthropometry and insulin resistance but not with low cardiorespiratory fitness in adolescents.J Endocrinol Invest. 2024 Feb;47(2):307-314. doi: 10.1007/s40618-023-02145-w. Epub 2023 Jun 23. J Endocrinol Invest. 2024. PMID: 37351836
-
Association between cardiorespiratory fitness and cardiometabolic risk factors in Brazilian children and adolescents: the mediating role of obesity parameters.Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021 May;41(2):93-102. doi: 10.1080/20469047.2020.1838758. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021. PMID: 33112727
-
Adiponectin concentration and cardiometabolic risk factors: the moderator role of cardiorespiratory fitness in adolescents.Eur J Pediatr. 2024 Nov;183(11):4847-4855. doi: 10.1007/s00431-024-05761-7. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Eur J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39251446
-
Obesity, central adiposity and cardiometabolic risk factors in children and adolescents: a family-based study.Pediatr Obes. 2014 Jun;9(3):e58-e62. doi: 10.1111/j.2047-6310.2014.218.x. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Pediatr Obes. 2014. PMID: 24677702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adolescent cardiometabolic risk scores: A scoping review.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2022 Dec;32(12):2669-2676. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2022.08.022. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2022. PMID: 36153209
Cited by
-
The relationship between weight-adjusted-waist index and suicidal ideation: evidence from NHANES.Eat Weight Disord. 2024 May 14;29(1):37. doi: 10.1007/s40519-024-01666-4. Eat Weight Disord. 2024. PMID: 38743203 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

