Comparison of lung ultrasound and chest radiography for detecting pneumonia in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38263086
- PMCID: PMC10804756
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-024-01583-3
Comparison of lung ultrasound and chest radiography for detecting pneumonia in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Lung ultrasound (LUS) is recommended as a reliable diagnostic alternative to chest X-ray (CXR) for detecting pneumonia in children.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases were used to identify eligible studies from their inception until April 2023. The investigated diagnostic parameters included sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUC).
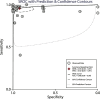
Results: Twenty-six studies involving 3,401 children were selected for meta-analysis. The sensitivity, specificity, PLR, NLR, DOR, and AUC of LUS for detecting pneumonia in children were 0.95, 0.92, 12.31, 0.05, 108.53, and 0.98, respectively, while the sensitivity, specificity, PLR, NLR, DOR, and AUC of CXR were 0.92, 0.93, 24.63, 0.08, 488.54, and 0.99, respectively. The sensitivity of LUS was higher than that of CXR for detecting pneumonia in children (ratio: 1.03; 95% CI: 1.01-1.06; P = 0.018), whereas the DOR of LUS was significantly lower than that of CXR (ratio: 0.22; 95% CI: 0.06-0.85; P = 0.028).
Conclusions: This study found that the diagnostic performance of LUS was comparable to that of CXR for detecting pneumonia, and the sensitivity of LUS was superior to that of CXR.
Keywords: Chest X-ray; Children; Lung ultrasound; Meta-analysis; Pneumonia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparing the Diagnostic Performance of Lung Ultrasonography and Chest Radiography for Detecting Pneumothorax in Patients with Trauma: A Meta-Analysis.Respiration. 2025;104(3):161-175. doi: 10.1159/000540777. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Respiration. 2025. PMID: 39348819 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumonia Lung Ultrasound Score (PLUS): A New Tool for Detecting Pneumonia in the Oldest Patients.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020 Dec;68(12):2855-2862. doi: 10.1111/jgs.16783. Epub 2020 Aug 17. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020. PMID: 33264442
-
Accuracy of Lung Ultrasound Compared to Chest Radiography for Diagnosing Pneumonia in Children: A Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional Study.Ethiop J Health Sci. 2024 Oct;34(Spec Iss 1):47-52. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v34i1.8S. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2024. PMID: 39735523 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Point-of-Care Lung Ultrasonography and Chest Radiography in Adults With Symptoms Suggestive of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Mar 1;2(3):e190703. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.0703. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 30874784 Free PMC article.
-
Lung ultrasound vs chest radiography in the diagnosis of children pneumonia: Systematic evidence.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Dec 11;99(50):e23671. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023671. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33327356 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of the accuracy of lung ultrasound and chest radiography in diagnosing community acquired pneumonia in children.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2024 Dec;59(12):3130-3147. doi: 10.1002/ppul.27221. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2024. PMID: 39239917 Free PMC article.
-
Echoes of change: lung ultrasound revolutionizing neonatal and pediatric respiratory care.Pediatr Radiol. 2025 Jul 1. doi: 10.1007/s00247-025-06300-8. Online ahead of print. Pediatr Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40590948 Review.
References
-
- Organization WH. April : Children: improving survival and well-being [updated September 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/children-reducing-morta.... Accessed 2023.
-
- House DR, Rijal S, Adhikari S, Cooper ML, Hohl CM. Prospective evaluation of World Health Organization guidelines for diagnosis of pneumonia in children presenting to an emergency department in a resource-limited setting. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2020;40(4):227–30. doi: 10.1080/20469047.2020.1815483. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chavez MA, Naithani N, Gilman RH, Tielsch JM, Khatry S, Ellington LE, Miranda JJ, Gurung G, Rodriguez S, Checkley W. Agreement between the World Health Organization Algorithm and Lung consolidation identified using point-of-care Ultrasound for the diagnosis of Childhood Pneumonia by General practitioners. Lung. 2015;193(4):531–8. doi: 10.1007/s00408-015-9730-x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous