Advancing patient-centered research practices in a pragmatic patient-level randomized clinical trial: A thematic analysis of stakeholder engagement in Emergency Medicine Palliative Care Access (EMPallA)
- PMID: 38263088
- PMCID: PMC10807180
- DOI: 10.1186/s40900-023-00539-x
Advancing patient-centered research practices in a pragmatic patient-level randomized clinical trial: A thematic analysis of stakeholder engagement in Emergency Medicine Palliative Care Access (EMPallA)
Abstract
Background: Involving patient and community stakeholders in clinical trials adds value by ensuring research prioritizes patient goals both in conduct of the study and application of the research. The use of stakeholder committees and their impact on the conduct of a multicenter clinical trial have been underreported clinically and academically. The aim of this study is to describe how Study Advisory Committee (SAC) recommendations were implemented throughout the Emergency Medicine Palliative Care Access (EMPallA) trial. EMPallA is a multi-center, pragmatic two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) comparing the effectiveness of nurse-led telephonic case management and specialty, outpatient palliative care of older adults with advanced illness.
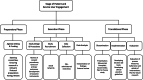
Methods: A SAC consisting of 18 individuals, including patients with palliative care experience, members of healthcare organizations, and payers was convened for the EMPallA trial. The SAC engaged in community-based participatory research and assisted in all aspects from study design to dissemination. The SAC met with the research team quarterly and annually from project inception to dissemination. Using meeting notes and recordings we completed a qualitative thematic analysis using an iterative process to develop themes and subthemes to summarize SAC recommendations throughout the project's duration.
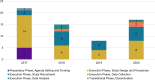
Results: The SAC convened 16 times between 2017 and 2020. Over the course of the project, the SAC provided 41 unique recommendations. Twenty-six of the 41 (63%) recommendations were adapted into formal Institutional Review Board (IRB) study modifications. Recommendations were coded into four major themes: Scientific, Pragmatic, Resource and Dissemination. A majority of the recommendations were related to either the Scientific (46%) or Pragmatic (29%) themes. Recommendations were not mutually exclusive across three study phases: Preparatory, execution and translational. A vast majority (94%) of the recommendations made were related to the execution phase. Major IRB study modifications were made based on their recommendations including data collection of novel dependent variables and expanding recruitment to Spanish-speaking patients.
Conclusions: Our study provides an example of successful integration of a SAC in the conduct of a pragmatic, multi-center RCT. Future trials should engage with SACs in all study phases to ensure trials are relevant, inclusive, patient-focused, and attentive to gaps between health care and patient and family needs.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT03325985, 10/30/2017.
Keywords: Palliative care; Patient and public involvement; Research design; Stakeholder participation; Study Advisory Committee.
Plain language summary
Clinical research should involve patient and community stakeholder perspectives to make sure the study addresses questions important to the studied population. One way to do this is by creating a group of stakeholders who can advise on the conduct of a study. We assembled a Study Advisory Committee (SAC) for the Emergency Medicine Palliative Care Access (EMPallA) trial. The purpose of this clinical trial is to compare the effectiveness of nurse-led telephonic case management and specialty, outpatient palliative care of older adults with advanced illness. This paper describes how the SACs involvement translated into direct impacts on the EMPallA trial. The trial research team held regular meetings with the SAC throughout the trial process. Their involvement led to many significant changes in the trial, such as expanding recruitment inclusion criteria (Spanish-speaking patients), and including survey instruments to measure lonelines and caregiver burden. The SAC also devised strategies to overcome patient and caregiver recruitment and retention challenges, including the creation of patient-friendly materials and training for research coordinators. This study provides a successful example of how actively engaging patient and community stakeholders, through committee engagement, can promote patient priorities in all phases of a trial while facilitating patient recruitment and retention.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Turner-Stokes L, Rose H, Ashford S, Singer B. Patient engagement and satisfaction with goal planning: Impact on outcome from rehabilitation. Int J Therapy Rehabil. 2015;22(5):210–216. doi: 10.12968/ijtr.2015.22.5.210. - DOI
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

