Exosomal secreted SCIMP regulates communication between macrophages and neutrophils in pneumonia
- PMID: 38263143
- PMCID: PMC10805922
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-44714-4
Exosomal secreted SCIMP regulates communication between macrophages and neutrophils in pneumonia
Abstract
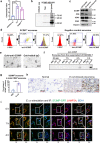
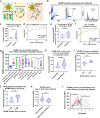
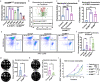
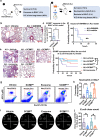
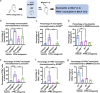
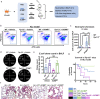
In pneumonia, the deficient or delayed pathogen clearance can lead to pathogen proliferation and subsequent overactive immune responses, inducing acute lung injury (ALI). While screening human genome coding genes using our peripheral blood cell chemotactic platform, we unexpectedly find SLP adaptor and CSK interacting membrane protein (SCIMP), a protein with neutrophil chemotactic activity secreted during ALI. However, the specific role of SCIMP in ALI remains unclear. In this study, we investigate the secretion of SCIMP in exosomes (SCIMPexo) by macrophages after bacterial stimulation, both in vitro and in vivo. We observe a significant increase in the levels of SCIMPexo in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and serum of pneumonia patients. We also find that bronchial perfusion with SCIMPexo or SCIMP N-terminal peptides increases the survival rate of the ALI model. This occurs due to the chemoattraction and activation of peripheral neutrophils dependent on formyl peptide receptor 1/2 (FPR1/2). Conversely, exosome suppressors and FPR1/2 antagonists decrease the survival rate in the lethal ALI model. Scimp-deficient and Fpr1/2-deficient mice also have lower survival rates and shorter survival times than wild-type mice. However, bronchial perfusion of SCIMP rescues Scimp-deficient mice but not Fpr1/2-deficient mice. Collectively, our findings suggest that the macrophage-SCIMP-FPRs-neutrophil axis plays a vital role in the innate immune process underlying ALI.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein C3 (ApoC3) facilitates NLRP3 mediated pyroptosis of macrophages through mitochondrial damage by accelerating of the interaction between SCIMP and SYK pathway in acute lung injury.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Feb 15;128:111537. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111537. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38232538
-
SCIMP is a universal Toll-like receptor adaptor in macrophages.J Leukoc Biol. 2020 Feb;107(2):251-262. doi: 10.1002/JLB.2MA0819-138RR. Epub 2019 Aug 29. J Leukoc Biol. 2020. PMID: 31468585
-
The Transmembrane Adaptor Protein SCIMP Facilitates Sustained Dectin-1 Signaling in Dendritic Cells.J Biol Chem. 2016 Aug 5;291(32):16530-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.717157. Epub 2016 Jun 10. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27288407 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the role of damage-associated molecular patterns and inflammatory responses in acute lung injury.Life Sci. 2022 Sep 15;305:120782. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120782. Epub 2022 Jul 6. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35809663 Review.
-
Pulmonary Innate Immune Response Determines the Outcome of Inflammation During Pneumonia and Sepsis-Associated Acute Lung Injury.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 4;11:1722. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01722. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849610 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
β-Catenin disruption decreases macrophage exosomal α-SNAP and impedes Treg differentiation in acute liver injury.JCI Insight. 2024 Nov 19;10(1):e182515. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.182515. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 39560996 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma-derived extracellular vesicles prime alveolar macrophages for autophagy and ferroptosis in sepsis-induced acute lung injury.Mol Med. 2025 Feb 4;31(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01111-x. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39901167 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenic cell death-related biomarkers in heart failure probed by transcriptome and single-cell sequencing.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 24;16:1560903. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1560903. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40630963 Free PMC article.
-
Cmpk2 Protects Against Acute Lung Injury in Mice.Lung. 2025 Jul 5;203(1):74. doi: 10.1007/s00408-025-00829-z. Lung. 2025. PMID: 40616692
-
Gene Regulation of Neutrophils Mediated Liver and Lung Injury through NETosis in Acute Pancreatitis.Inflammation. 2025 Feb;48(1):393-411. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02071-w. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 38884700
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81700099/National Science Foundation of China | National Natural Science Foundation of China-Yunnan Joint Fund (NSFC-Yunnan Joint Fund)
- 82072046/National Science Foundation of China | National Natural Science Foundation of China-Yunnan Joint Fund (NSFC-Yunnan Joint Fund)
- 81970536/National Science Foundation of China | National Natural Science Foundation of China-Yunnan Joint Fund (NSFC-Yunnan Joint Fund)
- 82271884/National Science Foundation of China | National Natural Science Foundation of China-Yunnan Joint Fund (NSFC-Yunnan Joint Fund)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

