Gastrointestinal bleeding in children: diagnostic approach
- PMID: 38263189
- PMCID: PMC10807079
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-024-01592-2
Gastrointestinal bleeding in children: diagnostic approach
Abstract
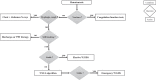
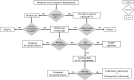
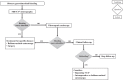
Different conditions may underlie gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB) in children. The estimated prevalence of GIB in children is 6.4%, with spontaneous resolution in approximately 80% of cases. Nonetheless, the initial approach plays a pivotal role in determining the prognosis. The priority is the stabilization of hemodynamic status, followed by a systematic diagnostic approach. GIB can originate from either upper or lower gastrointestinal tract, leading to a broad differential diagnosis in infants and children. This includes benign and self-limiting disorders, alongside serious conditions necessitating immediate treatment. We performed a nonsystematic review of the literature, in order to describe the variety of conditions responsible for GIB in pediatric patients and to outline diagnostic pathways according to patients' age, suspected site of bleeding and type of bleeding which can help pediatricians in clinical practice. Diagnostic modalities may include esophagogastroduodenoscopy and colonoscopy, abdominal ultrasonography or computed tomography and, when necessary, magnetic resonance imaging. In this review, we critically assess these procedures, emphasizing their respective advantages and limitations concerning specific clinical scenarios.
Keywords: Abdominal CT; Abdominal US; Endoscopy; Gastrointestinal bleeding; Hematemesis; Hematochezia; MR; Melena; Pediatric.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

