Green and environmentally friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial properties from some medicinal plants
- PMID: 38263231
- PMCID: PMC10807138
- DOI: 10.1186/s12896-023-00828-z
Green and environmentally friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial properties from some medicinal plants
Abstract
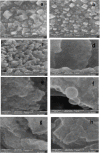
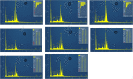
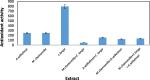
Recently there have been a variety of methods to synthesize silver nanoparticles, among which the biosynthesis method is more noticeable due to features like being eco-friendly, simple, and cost-efficient. The present study aims for the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from the extract of the three plants A. wilhelmsi, M. chamomilla, and C. longa; moreover, it pledges to measure the antibacterial activity against some variants causing a skin rash. The morphology and size of the synthesized silver nanoparticles were evaluated by UV.vis, XRD, SEM, and FTIR analyses. Then results showed a color alteration from light yellow to dark brown and the formation of silver nanoparticles. The absorption peak with the wavelength of approximately 450 nm resulting from the Spectrophotometry analysis confirmed the synthesis of silver nanoparticles. The presence of strong and wide peaks in FTIR indicated the presence of OH groups. The SEM results showed that most synthesized nanoparticles had a spherical angular structure and their size was about 10 to 20 nm. The highest inhibition power was demonstrated by silver nanoparticles synthesized from the extract combined from all three species against Gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis (23 mm) which had a performance far more powerful than the extract. Thus, it can be understood that the nanoparticles synthesized from these three species can act as potential environment-friendly alternatives to inhibit some variations causing skin disorders; an issue that calls for further clinical studies.
Keywords: Anti-microbial activity; Extract; Green synthesis; Nanotechnology; Wound healing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


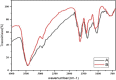
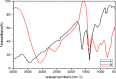
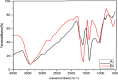
References
-
- Bishnoi S, Kumar A, Selvaraj R. Facile synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles using inedible Cynometra ramiflora fruit extract waste and their photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. Mater Res Bull. 2018;97:121–127. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.08.040. - DOI
-
- Sabzali Parikhani R, Sadighi H, Bijani M. Ecological Consequences of Nanotechnology in Agriculture: Researchers’ Perspective. J Agric Sci Technol. 2018;20(2):205–219.
-
- Bagherzade G, Tavakoli MM, Namaei MH. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) wastages and its antibacterial activity against six bacteria. Asian Pac Tropi Biomed. 2017;7(3):227–233. doi: 10.1016/j.apjtb.2016.12.014. - DOI
-
- Khan I, Saeed K, Khan I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab J Chem. 2019;12(7):908–931. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011. - DOI
-
- Saha J, Begum A, Mukherjee A, Kumar S. A novel green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their catalytic action in reduction of Methylene Blue dye. Sustain Environ Res. 2017;27(5):245–250. doi: 10.1016/j.serj.2017.04.003. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

