Desmopressin to reduce periprocedural bleeding and transfusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38263259
- PMCID: PMC10804695
- DOI: 10.1186/s13741-023-00358-4
Desmopressin to reduce periprocedural bleeding and transfusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
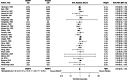
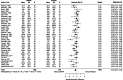
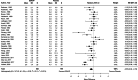
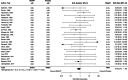
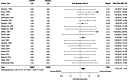
We systematically reviewed the literature to investigate the effects of peri-procedural desmopressin in patients without known inherited bleeding disorders undergoing surgery or other invasive procedures. We included 63 randomized trials (4163 participants) published up to February 1, 2023. Seven trials were published after a 2017 Cochrane systematic review on this topic. There were 38 trials in cardiac surgery, 22 in noncardiac surgery, and 3 in non-surgical procedures. Meta-analyses demonstrated that desmopressin likely does not reduce the risk of receiving a red blood cell transfusion (25 trials, risk ratio [RR] 0.95, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.86 to 1.05) and may not reduce the risk of reoperation due to bleeding (22 trials, RR 0.75, 95% CI 0.47 to 1.19) when compared to placebo or usual care. However, we demonstrated significant reductions in number of units of red blood cells transfused (25 trials, mean difference -0.55 units, 95% CI - 0.94 to - 0.15), total volume of blood loss (33 trials, standardized mean difference - 0.40 standard deviations; 95% CI - 0.56 to - 0.23), and the risk of bleeding events (2 trials, RR 0.45, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.84). The certainty of evidence of these findings was generally low. Desmopressin increased the risk of clinically significant hypotension that required intervention (19 trials, RR 2.15, 95% CI 1.36 to 3.41). Limited evidence suggests that tranexamic acid is more effective than desmopressin in reducing transfusion risk (3 trials, RR 2.38 favoring tranexamic acid, 95% CI 1.06 to 5.39) and total volume of blood loss (3 trials, mean difference 391.7 mL favoring tranexamic acid, 95% CI - 93.3 to 876.7 mL). No trials directly informed the safety and hemostatic efficacy of desmopressin in advanced kidney disease. In conclusion, desmopressin likely reduces periprocedural blood loss and the number of units of blood transfused in small trials with methodologic limitations. However, the risk of hypotension needs to be mitigated. Large trials should evaluate desmopressin alongside tranexamic acid and enroll patients with advanced kidney disease.
Keywords: Bleeding; Desmopressin; Systematic review; Transfusion.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Altun G, Hemşinli D, Pulathan Z, Civelek A. Emergency coronary bypass surgery in patients under the influence of dualantiplatelet therapy: effects of tranexamic acid and desmopressin acetate. Turk J Med Sci. 2017;47(6):1708-14. 10.3906/sag-1612-140. - PubMed
-
- Bignami E, Cattaneo M, Crescenzi G, et al. Desmopressin after cardiac surgery in bleeding patients A multicenter randomized trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2016;60(892):900. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

