The m6A demethylases FTO and ALKBH5 aggravate the malignant progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by coregulating ARHGAP35
- PMID: 38263362
- PMCID: PMC10806234
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-024-01810-0
The m6A demethylases FTO and ALKBH5 aggravate the malignant progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by coregulating ARHGAP35
Abstract
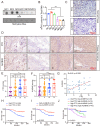
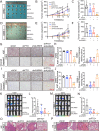
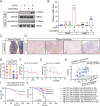
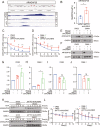
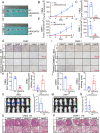
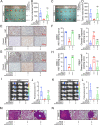
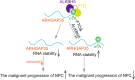
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is an RNA modification that can be removed by demethylases [fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) and AlkB homolog 5 (ALKBH5)], which regulate gene expression and cell function. We show that m6A levels and m6A demethylase levels are altered in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) tissues vs. normal tissues. High FTO and ALKBH5 predict a poor prognosis in NPC patients. Silencing FTO and ALKBH5 inhibited the malignant behavior of patient-derived NPC cells in a short time. However, as time progressed, the inhibitory effect of FTO or ALKBH5 was weakened, and the cosilencing of FTO and ALKBH5 maintained a better inhibitory effect. Combined transcriptome and m6A-seq analysis revealed a downstream target gene that was jointly regulated by FTO and ALKBH5 in NPC, and ARHGAP35 was chosen to do further study. The synergistic silencing of FTO and ALKBH5 increased the methylation level on the mRNA CDS of a new transcription factor (ARHGAP35) and positively regulate the protein coding capacity and mRNA stability of ARHGAP35, thus leading to increased expression of ARHGAP35 and inhibition of the malignant phenotype of tumor cells. Our study revealed that the growth and metastasis of NPC can be stably inhibited through synergistic silencing of the demethylases FTO and ALKBH5, which play a positive role in the treatment of NPC by regulating the downstream transcript ARHGAP35 and increasing its m6A level.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A study of RNA m6A demethylases in oral epithelial dysplasia and oral squamous cell carcinoma.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023 Mar-Apr;13(2):111-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2022.12.003. Epub 2022 Dec 10. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023. PMID: 36582218 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulated FTO and ALKBH5 co-operatively activates FOXO signaling through m6A methylation modification in HK2 mRNA mediated by IGF2BP2 to enhance glycolysis in colorectal cancer.Cell Biosci. 2023 Aug 14;13(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01100-9. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37580808 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Seq data of ALKBH5 and FTO double knockout HEK293T human cells.Data Brief. 2022 Apr 20;42:108187. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2022.108187. eCollection 2022 Jun. Data Brief. 2022. PMID: 35516002 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances of m6A Demethylases Inhibitors and Their Biological Functions in Human Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 22;23(10):5815. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105815. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the m6A demethylases FTO and ALKBH5 : structural, biological function, and inhibitor development.Cell Biosci. 2024 Aug 27;14(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01286-6. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39192357 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FTO-mediated m6A demethylation of SERPINE1 mRNA promotes tumor progression in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Jan 31;14(1):595-612. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2024-2507. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39974406 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic marvels: exploring the landscape of colorectal cancer treatment through cutting-edge epigenetic-based drug strategies.Clin Epigenetics. 2025 Feb 22;17(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13148-025-01844-w. Clin Epigenetics. 2025. PMID: 39987205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of N6-methyladenosine methylation in head and neck cancer and its regulation of innate immune pathways.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 30;15:1458884. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1458884. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39403369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential control of RNA demethylase activity and selectivity by cofactor ascorbate.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 8:2025.05.06.652568. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.06.652568. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40654844 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Emerging roles of N6-methyladenosine in arsenic-induced toxicity.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 17;10(22):e40473. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40473. eCollection 2024 Nov 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39641074 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
- 82372977/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82173288/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81972554/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- BK20201208/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

