Impact of technological advances in treatment planning, image guidance, and treatment delivery on target margin design for prostate cancer radiotherapy: an updated review
- PMID: 38263844
- PMCID: PMC11027310
- DOI: 10.1093/bjr/tqad041
Impact of technological advances in treatment planning, image guidance, and treatment delivery on target margin design for prostate cancer radiotherapy: an updated review
Abstract
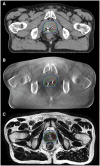
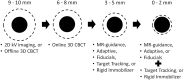
Recent innovations in image guidance, treatment delivery, and adaptive radiotherapy (RT) have created a new paradigm for planning target volume (PTV) margin design for patients with prostate cancer. We performed a review of the recent literature on PTV margin selection and design for intact prostate RT, excluding post-operative RT, brachytherapy, and proton therapy. Our review describes the increased focus on prostate and seminal vesicles as heterogenous deforming structures with further emergence of intra-prostatic GTV boost and concurrent pelvic lymph node treatment. To capture recent innovations, we highlight the evolution in cone beam CT guidance, and increasing use of MRI for improved target delineation and image registration and supporting online adaptive RT. Moreover, we summarize new and evolving image-guidance treatment platforms as well as recent reports of novel immobilization strategies and motion tracking. Our report also captures recent implementations of artificial intelligence to support image guidance and adaptive RT. To characterize the clinical impact of PTV margin changes via model-based risk estimates and clinical trials, we highlight recent high impact reports. Our report focusses on topics in the context of PTV margins but also showcase studies attempting to move beyond the PTV margin recipes with robust optimization and probabilistic planning approaches. Although guidelines exist for target margins conventional using CT-based image guidance, further validation is required to understand the optimal margins for online adaptation either alone or combined with real-time motion compensation to minimize systematic and random uncertainties in the treatment of patients with prostate cancer.
Keywords: cone beam computed tomography; image guided radiation therapy; magnetic resonance imaging; planning target volume; prostate cancer; radiation therapy.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Institute of Radiology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reduction of PTV margins for elective pelvic lymph nodes in online adaptive radiotherapy of prostate cancer patients.Acta Oncol. 2023 Oct;62(10):1208-1214. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2023.2252584. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Acta Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37682727
-
PTV margin analysis for prostate patients treated with initial pelvic nodal IMRT and prostate proton boost.Phys Med Biol. 2019 Feb 8;64(4):04NT04. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/aafd75. Phys Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 30630135
-
PTV margin definition in hypofractionated IGRT of localized prostate cancer using cone beam CT and orthogonal image pairs with fiducial markers.Radiat Oncol. 2014 Nov 11;9:229. doi: 10.1186/s13014-014-0229-z. Radiat Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25384898 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Clinical to planning target volume margins in prostate cancer radiotherapy].Cancer Radiother. 2016 Oct;20(6-7):629-39. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2016.07.095. Epub 2016 Sep 7. Cancer Radiother. 2016. PMID: 27614515 Review. French.
-
[Choice of optimal margins in prostate conformal radiotherapy].Cancer Radiother. 2013 Oct;17(5-6):461-9. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2013.06.031. Epub 2013 Aug 20. Cancer Radiother. 2013. PMID: 23973458 Review. French.
References
-
- Kerkmeijer LGW, Groen VH, Pos FJ, et al.Focal boost to the intraprostatic tumor in external beam radiotherapy for patients with localized prostate cancer: results from the FLAME randomized Phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(7):787-796. - PubMed
-
- Salembier C, Villeirs G, De Bari B, et al.ESTRO ACROP consensus guideline on CT- and MRI-based target volume delineation for primary radiation therapy of localized prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2018;127(1):49-61. - PubMed
-
- van Herk M. Errors and margins in radiotherapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2004;14(1):52-64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

