Intensive care unit-acquired weakness: Recent insights
- PMID: 38263973
- PMCID: PMC10800771
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jointm.2023.07.002
Intensive care unit-acquired weakness: Recent insights
Abstract
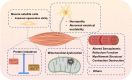
Intensive care unit-acquired weakness (ICU-AW) is a common complication in critically ill patients and is associated with a variety of adverse outcomes. These include the need for prolonged mechanical ventilation and ICU stay; higher ICU, in-hospital, and 1-year mortality; and increased in-hospital costs. ICU-AW is associated with multiple risk factors including age, underlying disease, severity of illness, organ failure, sepsis, immobilization, receipt of mechanical ventilation, and other factors related to critical care. The pathological mechanism of ICU-AW remains unclear and may be considerably varied. This review aimed to evaluate recent insights into ICU-AW from several aspects including risk factors, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment strategies; this provides new perspectives for future research.
Keywords: Intensive care unit-acquired weakness; Mechanism; Muscle atrophy; Muscle weakness; Risk factor; Treatment.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Chinese Medical Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

