Memory consolidation in honey bees is enhanced by down-regulation of Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule and changes its alternative splicing
- PMID: 38264345
- PMCID: PMC10803435
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1322808
Memory consolidation in honey bees is enhanced by down-regulation of Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule and changes its alternative splicing
Abstract
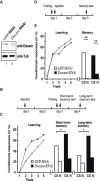
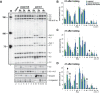
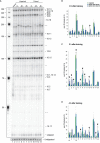
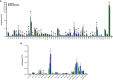
Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule (Dscam) gene encodes a cell adhesion molecule required for neuronal wiring. A remarkable feature of arthropod Dscam is massive alternative splicing generating thousands of different isoforms from three variable clusters of alternative exons. Dscam expression and diversity arising from alternative splicing have been studied during development, but whether they exert functions in adult brains has not been determined. Here, using honey bees, we find that Dscam expression is critically linked to memory retention as reducing expression by RNAi enhances memory after reward learning in adult worker honey bees. Moreover, alternative splicing of Dscam is altered in all three variable clusters after learning. Since identical Dscam isoforms engage in homophilic interactions, these results suggest a mechanism to alter inclusion of variable exons during memory consolidation to modify neuronal connections for memory retention.
Keywords: Dscam; RNA interference (gene silencing); alternative splicing; honey bee; learning and memory.
Copyright © 2024 Ustaoglu, McQuarrie, Rochet, Dix, Haussmann, Arnold, Devaud and Soller.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring perspectives of Dscam for cognitive deficits: a review of multifunction for regulating neural wiring in homeostasis.Front Mol Neurosci. 2025 May 2;18:1575348. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2025.1575348. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40385132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative splicing of the Drosophila Dscam pre-mRNA is both temporally and spatially regulated.Genetics. 2001 Oct;159(2):599-608. doi: 10.1093/genetics/159.2.599. Genetics. 2001. PMID: 11606537 Free PMC article.
-
A honey bee Dscam family member, AbsCAM, is a brain-specific cell adhesion molecule with the neurite outgrowth activity which influences neuronal wiring during development.Eur J Neurosci. 2007 Jan;25(1):168-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05270.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17241278
-
Srrm234, but not canonical SR and hnRNP proteins, drive inclusion of Dscam exon 9 variable exons.RNA. 2019 Oct;25(10):1353-1365. doi: 10.1261/rna.071316.119. Epub 2019 Jul 10. RNA. 2019. PMID: 31292260 Free PMC article.
-
Somatic and Germline Diversification of a Putative Immunoreceptor within One Phylum: Dscam in Arthropods.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2015;57:131-58. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-20819-0_6. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2015. PMID: 26537380 Review.
Cited by
-
Phylogenomic instructed target analysis reveals ELAV complex binding to multiple optimally spaced U-rich motifs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Nov 11;52(20):12712-12726. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae826. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39319593 Free PMC article.
-
From Biomphalaria glabrata to Drosophila melanogaster and Anopheles gambiae: the diversity and role of FREPs and Dscams in immune response.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 30;16:1579905. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1579905. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40370466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring perspectives of Dscam for cognitive deficits: a review of multifunction for regulating neural wiring in homeostasis.Front Mol Neurosci. 2025 May 2;18:1575348. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2025.1575348. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40385132 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alberini C. M., Ghirardi M., Metz R., Kandel E. R. (1994). C/EBP is an immediate-early gene required for the consolidation of long-term facilitation in Aplysia. Cell 76 1099–1114. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

