The Role of Rho Kinase Inhibitors in Corneal Diseases
- PMID: 38264539
- PMCID: PMC10804875
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S435522
The Role of Rho Kinase Inhibitors in Corneal Diseases
Abstract
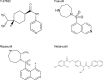
The cornea, as the outermost layer of the eye, plays a crucial role in vision by focusing light onto the retina. Various diseases and injuries can compromise its clarity, leading to impaired vision. This review aims to provide a thorough overview of the pharmacological properties, therapeutic potential and associated risks of Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) inhibitors in the management of corneal diseases. The article focuses on four key ROCK inhibitors: Y-27632, fasudil, ripasudil, and netarsudil, providing a comparative examination. Studies supporting the use of ROCK inhibitors highlight their efficacy across diverse corneal conditions. In Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy, studies on the application of Y-27632, ripasudil, and netarsudil demonstrated noteworthy enhancements in corneal clarity, endothelial cell density, and visual acuity. In pseudophakic bullous keratopathy, the injection of Y-27632 together with cultured corneal endothelial cells into the anterior chamber lead to enhanced corneal endothelial cell density and improved visual acuity. Animal models simulating chemical injury to the cornea showed a reduction of neovascularization and epithelial defects after application of fasudil and in a case of iridocorneal endothelial syndrome netarsudil improved corneal edema. Addressing safety considerations, netarsudil and ripasudil, both clinically approved, exhibit adverse events such as conjunctival hyperemia, conjunctival hemorrhage, cornea verticillata, conjunctivitis, and blepharitis. Monitoring patients during treatment becomes crucial to balancing the potential therapeutic benefits with these associated risks. In conclusion, ROCK inhibitors, particularly netarsudil and ripasudil, offer promise in managing corneal diseases. The comparative analysis of their pharmacological properties and studies supporting their efficacy underscore their potential therapeutic significance. However, ongoing research is paramount to comprehensively understand their safety profiles and long-term outcomes in diverse corneal conditions, guiding their optimal application in clinical practice.
Keywords: Fuchs’ endothelial corneal dystrophy; cornea; corneal diseases; corneal dystrophies; corneal transplantation; rho kinase inhibitors.
© 2024 Futterknecht et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Bowling B. Kanski’s Clinical Ophthalmology. Edinburgh: Elsevier; 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical