Effective evaluation of HGcnMLP method for markerless 3D pose estimation of musculoskeletal diseases patients based on smartphone monocular video
- PMID: 38264579
- PMCID: PMC10803458
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1335251
Effective evaluation of HGcnMLP method for markerless 3D pose estimation of musculoskeletal diseases patients based on smartphone monocular video
Abstract
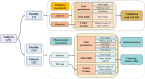
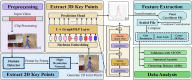
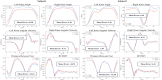
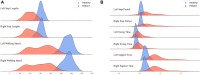
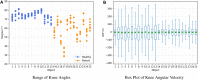
Markerless pose estimation based on computer vision provides a simpler and cheaper alternative to human motion capture, with great potential for clinical diagnosis and remote rehabilitation assessment. Currently, the markerless 3D pose estimation is mainly based on multi-view technology, while the more promising single-view technology has defects such as low accuracy and reliability, which seriously limits clinical application. This study proposes a high-resolution graph convolutional multilayer perception (HGcnMLP) human 3D pose estimation framework for smartphone monocular videos and estimates 15 healthy adults and 12 patients with musculoskeletal disorders (sarcopenia and osteoarthritis) gait spatiotemporal, knee angle, and center-of-mass (COM) velocity parameters, etc., and compared with the VICON gold standard system. The results show that most of the calculated parameters have excellent reliability (VICON, ICC (2, k): 0.853-0.982; Phone, ICC (2, k): 0.839-0.975) and validity (Pearson r: 0.808-0.978, p0.05). In addition, the proposed system can better evaluate human gait balance ability, and the K-means++ clustering algorithm can successfully distinguish patients into different recovery level groups. This study verifies the potential of a single smartphone video for 3D human pose estimation for rehabilitation auxiliary diagnosis and balance level recognition, and is an effective attempt at the clinical application of emerging computer vision technology. In the future, it is hoped that the corresponding smartphone program will be developed to provide a low-cost, effective, and simple new tool for remote monitoring and rehabilitation assessment of patients.
Keywords: high-resolution graph convolutional multilayer perception (HGcnMLP); markerless pose estimation; musculoskeletal disorders; rehabilitation assessment; smartphone monocular video.
Copyright © 2024 Hu, Diao, Wang, Li, He, Ning, Lou, Li and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Arthur D., Vassilvitskii S. (2007). “K-means++ the advantages of careful seeding,” in Proceedings of the eighteenth annual ACM-SIAM symposium on Discrete algorithms, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, January 7-9, 2007, 1027–1035.
-
- Avogaro A., Cunico F., Rosenhahn B., Setti F. (2023). Markerless human pose estimation for biomedical applications: a survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.00519 .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

