Functional microRNA-targeting drug discovery by graph-based deep learning
- PMID: 38264717
- PMCID: PMC10801238
- DOI: 10.1016/j.patter.2023.100909
Functional microRNA-targeting drug discovery by graph-based deep learning
Abstract
MicroRNAs are recognized as key drivers in many cancers but targeting them with small molecules remains a challenge. We present RiboStrike, a deep-learning framework that identifies small molecules against specific microRNAs. To demonstrate its capabilities, we applied it to microRNA-21 (miR-21), a known driver of breast cancer. To ensure selectivity toward miR-21, we performed counter-screens against miR-122 and DICER. Auxiliary models were used to evaluate toxicity and rank the candidates. Learning from various datasets, we screened a pool of nine million molecules and identified eight, three of which showed anti-miR-21 activity in both reporter assays and RNA sequencing experiments. Target selectivity of these compounds was assessed using microRNA profiling and RNA sequencing analysis. The top candidate was tested in a xenograft mouse model of breast cancer metastasis, demonstrating a significant reduction in lung metastases. These results demonstrate RiboStrike's ability to nominate compounds that target the activity of miRNAs in cancer.
Keywords: RNA-targeting drug discovery; artificial intelligence; deep learning; drug toxicity evaluation; graph convolutional neural network; in silico drug screening; microRNA inhibition; microRNA-21.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The work has been patented by the University of Central Florida (UCF) and the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) under the title of “Deep-Learning Based Methods for Virtual Screening of Molecules for Micro Ribonucleic Acid (miRNA) Drug Discovery” (application number: 63/309,132).
Figures
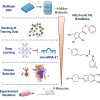
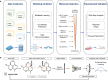
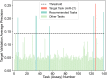
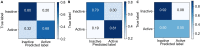
Update of
-
Functional microRNA-Targeting Drug Discovery by Graph-Based Deep Learning.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 16:2023.01.13.524005. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.13.524005. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Patterns (N Y). 2024 Jan 03;5(1):100909. doi: 10.1016/j.patter.2023.100909. PMID: 36711761 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Ma J., Dong C., Ji C. MicroRNA and drug resistance. Cancer Gene Ther. 2010;17:523–531. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

