Deep learning-based immunohistochemical estimation of breast cancer via ultrasound image applications
- PMID: 38264739
- PMCID: PMC10803514
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1263685
Deep learning-based immunohistochemical estimation of breast cancer via ultrasound image applications
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is the key global menace to women's health, which ranks first by mortality rate. The rate reduction and early diagnostics of breast cancer are the mainstream of medical research. Immunohistochemical examination is the most important link in the process of breast cancer treatment, and its results directly affect physicians' decision-making on follow-up medical treatment.
Purpose: This study aims to develop a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) method based on deep learning to classify breast ultrasound (BUS) images according to immunohistochemical results.
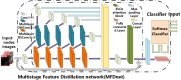
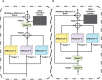
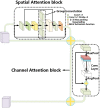
Methods: A new depth learning framework guided by BUS image data analysis was proposed for the classification of breast cancer nodes in BUS images. The proposed CAD classification network mainly comprised three innovation points. First, a multilevel feature distillation network (MFD-Net) based on CNN, which could extract feature layers of different scales, was designed. Then, the image features extracted at different depths were fused to achieve multilevel feature distillation using depth separable convolution and reverse depth separable convolution to increase convolution depths. Finally, a new attention module containing two independent submodules, the channel attention module (CAM) and the spatial attention module (SAM), was introduced to improve the model classification ability in channel and space.
Results: A total of 500 axial BUS images were retrieved from 294 patients who underwent BUS examination, and these images were detected and cropped, resulting in breast cancer node BUS image datasets, which were classified according to immunohistochemical findings, and the datasets were randomly subdivided into a training set (70%) and a test set (30%) in the classification process, with the results of the four immune indices output simultaneously from training and testing, in the model comparison experiment. Taking ER immune indicators as an example, the proposed model achieved a precision of 0.8933, a recall of 0.7563, an F1 score of 0.8191, and an accuracy of 0.8386, significantly outperforming the other models. The results of the designed ablation experiment also showed that the proposed multistage characteristic distillation structure and attention module were key in improving the accuracy rate.
Conclusion: The extensive experiments verify the high efficiency of the proposed method. It is considered the first classification of breast cancer by immunohistochemical results in breast cancer image processing, and it provides an effective aid for postoperative breast cancer treatment, greatly reduces the difficulty of diagnosis for doctors, and improves work efficiency.
Keywords: computer-aided diagnosis; deep learning; immunohistochemistry; neural network; node of breast cancer.
Copyright © 2024 Yan, Zhao, Duan, Qu, Shi, Wang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A VGG attention vision transformer network for benign and malignant classification of breast ultrasound images.Med Phys. 2022 Sep;49(9):5787-5798. doi: 10.1002/mp.15852. Epub 2022 Jul 30. Med Phys. 2022. PMID: 35866492
-
Diagnosis of cervical lymph node metastasis with thyroid carcinoma by deep learning application to CT images.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 26;13:1099104. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1099104. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36776294 Free PMC article.
-
An Edge-Based Selection Method for Improving Regions-of-Interest Localizations Obtained Using Multiple Deep Learning Object-Detection Models in Breast Ultrasound Images.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Sep 6;22(18):6721. doi: 10.3390/s22186721. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36146070 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-task learning for segmentation and classification of breast tumors from ultrasound images.Comput Biol Med. 2024 May;173:108319. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108319. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Comput Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 38513394
-
Semi-supervised segmentation of lesion from breast ultrasound images with attentional generative adversarial network.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020 Jun;189:105275. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.105275. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020. PMID: 31978805
References
-
- Cheng HD, Shan J, Ju. W, Guo YH, Zhang L. Automated breast cancer detection and classification using ultrasound images: A survey. Pattern Recognit (2009) 43:299–317. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2009.05.012 - DOI
-
- Park HJ, Kim SM, La Yun B, Jang M, Kim B, Jang JY, et al. . A computer-aided diagnosis system using artificial intelligence for diagnosing and characterizing breast masses on ultrasound: Added value for the inexperienced breast radiologist. Med (Baltimore) (2019) 98(3):e14146. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014146 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

