Efficacy and Safety of Elobixibat in Parkinson's Disease with Chronic Constipation: CONST-PD Study
- PMID: 38264844
- PMCID: PMC10982595
- DOI: 10.1002/mdc3.13972
Efficacy and Safety of Elobixibat in Parkinson's Disease with Chronic Constipation: CONST-PD Study
Abstract
Background: Chronic constipation is a common digestive complication of Parkinson's disease (PD).
Objectives: To verify the usefulness of elobixibat, an ileal bile acid transporter inhibitor, for chronic constipation in PD.
Methods: This double-blind, placebo-controlled study consisted of a 2-week observation/washout period and a 4-week treatment period. All patients received a Bowel Movement Diary at Week -2 and were allocated to elobixibat (10 mg) or placebo at Week 0. Patients visited at Weeks 2 and 4 to report daily spontaneous bowel movements (SBM), stool form, drug use, quality of life (QOL), and safety. Changes in these parameters were assessed.
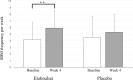
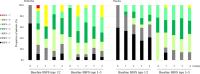
Results: The study included 38 patients in the elobixibat group and 39 in the placebo group, and 37 each completed the study. SBM frequency/week (mean ± standard deviation) increased significantly from 4.2 ± 2.6 at baseline to 5.9 ± 3.2 at Week 4 in the elobixibat group (P = 0.0079), but not in the placebo group (4.5 ± 2.7 to 5.3 ± 3.5; P = 0.0889). On analysis of covariance, the between-group difference in frequency changes at Week 4 (primary endpoint) was not significant after adjustment by baseline and sex (point estimate = 0.8; 95% confidence interval = -0.57 to 2.09, P = 0.2601), although a significant difference (P = 0.0011) was evidenced at Week 1 by a similar analysis. Stool form and scores of satisfaction and stigma were improved by elobixibat. Adverse events were as previously reported.
Conclusions: Elobixibat improved the SBM frequency, though the defined primary endpoint was not evidenced. QOL parameters (stool consistency and treatment satisfaction) were also improved. Elobixibat may have therapeutic benefits in PD patients suffering from chronic constipation.
Trial registration information: Trial Registration Number: JPRN-jRCTs031200172 (submitted: October 26, 2020; first patient enrolment: December 23, 2020; https://jrct.niph.go.jp/en-latest-detail/jRCTs031200172).
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; autonomic; clinical neurology; constipation; movement disorders; randomized trials.
© 2024 The Authors. Movement Disorders Clinical Practice published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Figures
References
-
- Fasano A, Visanji NP, Liu LWC, Lang AE, Pfeiffer RF. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol 2015;14:625–639. - PubMed
-
- Pfeiffer RF. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol 2003;2:107–116. - PubMed
-
- Stirpe P, Hoffman M, Badiali D, Colosimo C. Constipation: an emerging risk factor for Parkinson's disease? Eur J Neurol 2016;23:1606–1613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

