Liprin-α1 contributes to oncogenic MAPK signaling by counteracting ERK activity
- PMID: 38264964
- PMCID: PMC10920090
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.13593
Liprin-α1 contributes to oncogenic MAPK signaling by counteracting ERK activity
Abstract
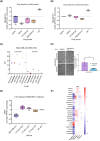
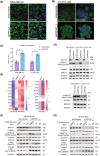
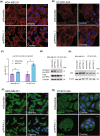
PTPRF interacting protein alpha 1 (PPFIA1) encodes for liprin-α1, a member of the leukocyte common antigen-related protein tyrosine phosphatase (LAR-RPTPs)-interacting protein family. Liprin-α1 localizes to adhesive and invasive structures in the periphery of cancer cells, where it modulates migration and invasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) and breast cancer. To study the possible role of liprin-α1 in anticancer drug responses, we screened a library of oncology compounds in cell lines with high endogenous PPFIA1 expression. The compounds with the highest differential responses between high PPFIA1-expressing and silenced cells across cell lines were inhibitors targeting mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) signaling. KRAS proto-oncogene, GTPase (KRAS)-mutated MDA-MB-231 cells were more resistant to trametinib upon PPFIA1 knockdown compared with control cells. In contrast, liprin-α1-depleted HNSCC cells with low RAS activity showed a context-dependent response to MEK/ERK inhibitors. Importantly, we showed that liprin-α1 depletion leads to increased p-ERK1/2 levels in all our studied cell lines independent of KRAS mutational status, suggesting a role of liprin-α1 in the regulation of MAPK oncogenic signaling. Furthermore, liprin-α1 depletion led to more pronounced redistribution of RAS proteins to the cell membrane. Our data suggest that liprin-α1 is an important contributor to oncogenic RAS/MAPK signaling, and the status of liprin-α1 may assist in predicting drug responses in cancer cells in a context-dependent manner.
Keywords: MEK/ERK inhibitor; MEK/ERK signaling pathway; RAS; drug screen; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; liprin-α1.
© 2024 The Authors. Molecular Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Serra‐Pages C, Medley QG, Tang M, Hart A, Streuli M. Liprins, a family of LAR transmembrane protein‐tyrosine phosphatase‐interacting proteins. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(25):15611–15620. - PubMed
-
- Jarvinen AK, Autio R, Haapa‐Paananen S, Wolf M, Saarela M, Grénman R, et al. Identification of target genes in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by high‐resolution copy number and gene expression microarray analyses. Oncogene. 2006;25(52):6997–7008. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

