Rational Design of a Potential New Nematicide Targeting Chitin Deacetylase
- PMID: 38264997
- PMCID: PMC10853968
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05258
Rational Design of a Potential New Nematicide Targeting Chitin Deacetylase
Abstract
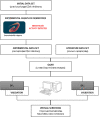
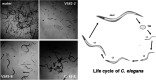
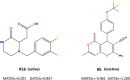
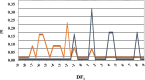
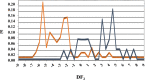
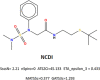
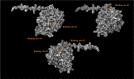
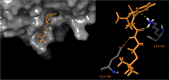
In a previously published study, the authors devised a molecular topology QSAR (quantitative structure-activity relationship) approach to detect novel fungicides acting as inhibitors of chitin deacetylase (CDA). Several of the chosen compounds exhibited noteworthy activity. Due to the close relationship between chitin-related proteins present in fungi and other chitin-containing plant-parasitic species, the authors decided to test these molecules against nematodes, based on their negative impact on agriculture. From an overall of 20 fungal CDA inhibitors, six showed to be active against Caenorhabditis elegans. These experimental results made it possible to develop two new molecular topology-based QSAR algorithms for the rational design of potential nematicides with CDA inhibitor activity for crop protection. Linear discriminant analysis was employed to create the two algorithms, one for identifying the chemo-mathematical pattern of commercial nematicides and the other for identifying nematicides with activity on CDA. After creating and validating the QSAR models, the authors screened several natural and synthetic compound databases, searching for alternatives to current nematicides. Finally one compound, the N2-(dimethylsulfamoyl)-N-{2-[(2-methyl-2-propanyl)sulfanyl]ethyl}-N2-phenylglycinamide or nematode chitin deacetylase inhibitor, was selected as the best candidate and was further investigated both in silico, through molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulations, and in vitro, through specific experimental assays. The molecule shows favorable binding behavior on the catalytic pocket of C. elegans CDA and the experimental assays confirm potential nematicide activity.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; QSAR; chitin deacetylase; molecular topology; nematicide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rational Design of Chitin Deacetylase Inhibitors for Sustainable Agricultural Use Based on Molecular Topology.J Agric Food Chem. 2022 Oct 19;70(41):13118-13131. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c02377. Epub 2022 Oct 4. J Agric Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 36194443 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Chitin Deacetylase Inhibitors through Structure-Based Virtual Screening and Biological Assays.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Apr 28;32(4):504-513. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2201.01009. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35131956 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of chitin/chitosan/chitosan oligosaccharide against plant pathogenic nematodes and potential modes of application in agriculture: A review.Carbohydr Polym. 2023 Apr 15;306:120592. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120592. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Carbohydr Polym. 2023. PMID: 36746583 Review.
-
Nematode Chitin and Application.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1142:209-219. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-7318-3_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31102248 Review.
-
Structure-Based Virtual Screening of Natural Products and Optimization for the Design and Synthesis of Novel CeCht1 Inhibitors as Nematicide Candidates.J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Jan 11;71(1):244-254. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06516. Epub 2022 Dec 28. J Agric Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 36579419
Cited by
-
Upgrading Strategies for Managing Nematode Pests on Profitable Crops.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jun 4;13(11):1558. doi: 10.3390/plants13111558. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38891366 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

