Distinct Clinical Effects of Two RP1L1 Hotspots in East Asian Patients With Occult Macular Dystrophy (Miyake Disease): EAOMD Report 4
- PMID: 38265784
- PMCID: PMC10810149
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.65.1.41
Distinct Clinical Effects of Two RP1L1 Hotspots in East Asian Patients With Occult Macular Dystrophy (Miyake Disease): EAOMD Report 4
Abstract
Purpose: To characterize the clinical effects of two RP1L1 hotspots in patients with East Asian occult macular dystrophy (OMD).
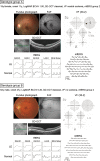
Methods: Fifty-one patients diagnosed with OMD harboring monoallelic pathogenic RP1L1 variants (Miyake disease) from Japan, South Korea, and China were enrolled. Patients were classified into two genotype groups: group A, p.R45W, and group B, missense variants located between amino acids (aa) 1196 and 1201. The clinical parameters of the two genotypes were compared, and deep learning based on spectral-domain optical coherence tomographic (SD-OCT) images was used to distinguish the morphologic differences.
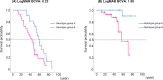
Results: Groups A and B included 29 and 22 patients, respectively. The median age of onset in groups A and B was 14.0 and 40.0 years, respectively. The median logMAR visual acuity of groups A and B was 0.70 and 0.51, respectively, and the survival curve analysis revealed a 15-year difference in vision loss (logMAR 0.22). A statistically significant difference was observed in the visual field classification, but no significant difference was found in the multifocal electroretinographic classification. High accuracy (75.4%) was achieved in classifying genotype groups based on SD-OCT images using machine learning.
Conclusions: Distinct clinical severities and morphologic phenotypes supported by artificial intelligence-based classification were derived from the two investigated RP1L1 hotspots: a more severe phenotype (p.R45W) and a milder phenotype (1196-1201 aa). This newly identified genotype-phenotype association will be valuable for medical care and the design of therapeutic trials.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of East Asian Patients with Occult Macular Dystrophy (Miyake Disease): East Asia Occult Macular Dystrophy Studies Report Number 1.Ophthalmology. 2019 Oct;126(10):1432-1444. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2019.04.032. Epub 2019 Apr 25. Ophthalmology. 2019. PMID: 31028767
-
Varied clinical presentations of RP1L1 variants in Chinese patients: a study of occult macular dystrophy and vitelliform macular dystrophy.BMC Ophthalmol. 2024 Aug 6;24(1):327. doi: 10.1186/s12886-024-03591-7. BMC Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39107704 Free PMC article.
-
Novel RP1L1 Variants and Genotype-Photoreceptor Microstructural Phenotype Associations in Cohort of Japanese Patients With Occult Macular Dystrophy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Sep 1;57(11):4837-46. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-19670. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27623337
-
Occult Macular Dystrophy: a case report and major review.Ophthalmic Genet. 2022 Oct;43(5):703-708. doi: 10.1080/13816810.2022.2089361. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Ophthalmic Genet. 2022. PMID: 35765812 Review.
-
Occult macular dystrophy.Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2015 Mar;59(2):71-80. doi: 10.1007/s10384-015-0371-7. Epub 2015 Feb 10. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25665791 Review.
Cited by
-
Review of Four Refined Clinical Entities in Hereditary Retinal Disorders from Japan.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 28;26(11):5166. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115166. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of RP1L1-Associated Retinopathy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Apr 1;66(4):7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.4.7. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40172514 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Distributions in Non-ABCA4 Autosomal Macular Dystrophies.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 May 1;65(5):9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.5.9. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38700873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miyake Y, Ichikawa K, Shiose Y, Kawase Y.. Hereditary macular dystrophy without visible fundus abnormality. Am J Ophthalmol. 1989; 108(3): 292–299. - PubMed
-
- Miyake Y, Horiguchi M, Tomita N, et al. .. Occult macular dystrophy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996; 122(5): 644–653. - PubMed
-
- Miyake Y, Tsunoda K.. Occult macular dystrophy. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2015; 59(2): 71–80. - PubMed
-
- Fujinami-Yokokawa YRA, Sergouniotis PI, Fujinaim K. Occult macular dystrophy. Vol. 1. In: Black GCM, Ashworth JL, Sergouniotis PI, eds. Clinical Ophthalmic Genetics and Genomics. Manchester, UK: Elsevier; 2022: 41–245.
-
- Fujinami K, Yang L, Joo K, et al. .. Clinical and genetic characteristics of East Asian patients with occult macular dystrophy (Miyake disease): east asia occult macular dystrophy studies report number 1. Ophthalmology. 2019; 126(10): 1432–1444. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

