Neutrophils in Physiology and Pathology
- PMID: 38265879
- PMCID: PMC11060889
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-051222-015009
Neutrophils in Physiology and Pathology
Abstract
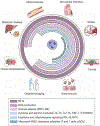
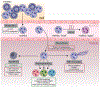
Infections, cardiovascular disease, and cancer are major causes of disease and death worldwide. Neutrophils are inescapably associated with each of these health concerns, by either protecting from, instigating, or aggravating their impact on the host. However, each of these disorders has a very different etiology, and understanding how neutrophils contribute to each of them requires understanding the intricacies of this immune cell type, including their immune and nonimmune contributions to physiology and pathology. Here, we review some of these intricacies, from basic concepts in neutrophil biology, such as their production and acquisition of functional diversity, to the variety of mechanisms by which they contribute to preventing or aggravating infections, cardiovascular events, and cancer. We also review poorly explored aspects of how neutrophils promote health by favoring tissue repair and discuss how discoveries about their basic biology inform the development of new therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: cancer; cardiovascular disease; infection; inflammation; neutrophil.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Kwok I, Becht E, Xia Y, Ng M, Teh YC, et al. 2020. Combinatorial Single-Cell Analyses of Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitor Heterogeneity Reveals an Early Uni-potent Neutrophil Progenitor. Immunity. 53(2):303–318.e5 - PubMed
-
- Evrard M, Kwok IWH, Chong SZ, Teng KWW, Becht E, et al. 2018. Developmental Analysis of Bone Marrow Neutrophils Reveals Populations Specialized in Expansion, Trafficking, and Effector Functions. Immunity. 48(2):364–379.e8 - PubMed
-
- Elsner J, Roesler J, Emmendörffer A, Zeidler C, Lohmann-Matthes M-L, Welte K. 1992. Altered function and surface marker expression of neutrophils induced by rhG-CSF treatment in severe congenital neutropenia. European Journal of Haematology. 48(1):10–19 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

