Arachidonic acid inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome is a mechanism to explain the anti-inflammatory effects of fasting
- PMID: 38265935
- PMCID: PMC10940735
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.113700
Arachidonic acid inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome is a mechanism to explain the anti-inflammatory effects of fasting
Abstract
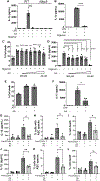
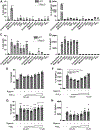
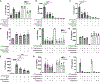
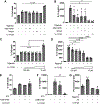
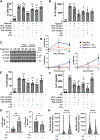
Elevated interleukin (IL)-1β levels, NLRP3 inflammasome activity, and systemic inflammation are hallmarks of chronic metabolic inflammatory syndromes, but the mechanistic basis for this is unclear. Here, we show that levels of plasma IL-1β are lower in fasting compared to fed subjects, while the lipid arachidonic acid (AA) is elevated. Lipid profiling of NLRP3-stimulated mouse macrophages shows enhanced AA production and an NLRP3-dependent eicosanoid signature. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs decreases eicosanoid, but not AA, production. It also reduces both IL-1β and IL-18 production in response to NLRP3 activation. AA inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activity in human and mouse macrophages. Mechanistically, AA inhibits phospholipase C activity to reduce JNK1 stimulation and hence NLRP3 activity. These data show that AA is an important physiological regulator of the NLRP3 inflammasome and explains why fasting reduces systemic inflammation and also suggests a mechanism to explain how nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs work.
Keywords: CP: Immunology; CP: Metabolism; NLRP3; eicosanoids; inflammasome; inflammation; lipidomics; metaflammation; prostaglandins.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests C.E.B. is a co-founder of Danger Bio, on the scientific advisory board of Nodthera and Related Sciences, and is a consultant for Janssen.
Figures
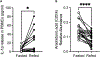

References
-
- Christ A, Lauterbach M, and Latz E (2019). Western Diet and the Immune System: An Inflammatory Connection. Immunity 51, 794–811. - PubMed
-
- Wiedemann SJ, Trimigliozzi K, Dror E, Meier DT, Molina-Tijeras JA, Rachid L, Le Foll C, Magnan C, Schulze F, Stawiski M, et al. (2022). The cephalic phase of insulin release is modulated by IL-1βeta. Cell Metab. 34, 991–1003.e6. - PubMed
-
- Misaki Y, Miyauchi R, Mochizuki K, Takabe S, Shimada M, Ichikawa Y, and Goda T (2010). Plasma interleukin-1beta concentrations are closely associated with fasting blood glucose levels in healthy and pre-clinical middle-aged nonoverweight and overweight Japanese men. Metabolism 59, 1465–1471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

