Risankizumab: Mechanism of action, clinical and translational science
- PMID: 38266061
- PMCID: PMC10777435
- DOI: 10.1111/cts.13706
Risankizumab: Mechanism of action, clinical and translational science
Abstract
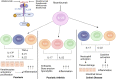
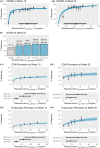
Risankizumab is a high-affinity neutralizing anti-interleukin (IL)-23 monoclonal antibody marketed in over 40 countries across the globe to treat several inflammatory diseases, such as plaque psoriasis (PsO), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and Crohn's disease (CD). This paper reviews the regulatory approval, mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics (PKs)/pharmacodynamics, immunogenicity, and clinical efficacy and safety data for risankizumab, focusing on the three main approved indications. Risankizumab binds to the p19 subunit of IL-23 and inhibits IL-23 from interacting with the IL-23 receptor and subsequent signaling. Biomarker data obtained following treatment with risankizumab in multiple indications provided supportive evidence for downstream blockade of IL-23 signaling associated with disease pathology. The PKs of risankizumab is linear and time-independent, consistent with typical IgG1 monoclonal antibodies, across all evaluated indications. Risankizumab exhibited positive exposure-response relationships for efficacy with no apparent exposure-dependent worsening in safety. Immunogenicity to risankizumab had no major clinical consequences for either efficacy or safety. Efficacy and safety of risankizumab have been established in PsO, PsA, and CD in the pivotal clinical trials where superior benefit/risk profiles were demonstrated compared to placebo and/or active comparators. Moreover, safety evaluations in open-label extension studies following long-term treatment with risankizumab showed stable and favorable safety profiles consistent with shorter-term studies. These data formed the foundation for risankizumab's marketing approvals to treat multiple inflammatory diseases across the globe.
© 2024 AbbVie Inc. Clinical and Translational Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employees of AbbVie and may hold AbbVie stock.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Risankizumab to treat moderately to severely active Crohn's disease in adults: an evaluation of trials and data.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Dec;17(12):1169-1183. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2023.2295496. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 38095092 Review.
-
Risankizumab in Adults with Psoriatic Arthritis.Skin Therapy Lett. 2023 Nov;28(6):1-6. Skin Therapy Lett. 2023. PMID: 38015960
-
Risankizumab: First Global Approval.Drugs. 2019 Jun;79(8):893-900. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-01136-7. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31098898 Review.
-
Risankizumab for the treatment of active psoriatic arthritis in adults.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2023 Jul-Dec;19(12):1435-1448. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2023.2265567. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37772959 Review.
-
Population Pharmacokinetics and Exposure-Response Analyses for Risankizumab in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis.Rheumatol Ther. 2022 Dec;9(6):1587-1603. doi: 10.1007/s40744-022-00495-0. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Rheumatol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36178584 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Authors' Reply to Wang et al., "Comment on 'Efficacy and Safety of Brodalumab, an Anti‑interleukin‑17 Receptor A Monoclonal Antibody, for Palmoplantar Pustulosis: 16‑Week Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial'".Am J Clin Dermatol. 2024 Nov;25(6):1025-1027. doi: 10.1007/s40257-024-00896-7. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 39405017 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Interleukin 23: Pathogenetic Involvement and Therapeutic Target for Ulcerative Colitis.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 28;14(13):4590. doi: 10.3390/jcm14134590. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40648967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Interleukin-23 Antagonists' Use in Crohn's Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Mar 22;18(4):447. doi: 10.3390/ph18040447. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the IL-23 Receptor Gene: A Promising Approach in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 16;26(10):4775. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104775. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and function of therapeutic antibodies approved by the US FDA in 2023.Antib Ther. 2024 Mar 19;7(2):132-156. doi: 10.1093/abt/tbae007. eCollection 2024 Apr. Antib Ther. 2024. PMID: 38617189 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Iwakura Y, Nakae S, Saijo S, Ishigame H. The roles of IL‐17A in inflammatory immune responses and host defense against pathogens. Immunol Rev. 2008;226:57‐79. - PubMed
-
- Liu Z, Yadav PK, Xu X, et al. The increased expression of IL‐23 in inflammatory bowel disease promotes intraepithelial and lamina propria lymphocyte inflammatory responses and cytotoxicity. J Leukoc Biol. 2011;89:597‐606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

