Apolipoprotein E secreted by astrocytes forms antiparallel dimers in discoidal lipoproteins
- PMID: 38266643
- PMCID: PMC10994765
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.12.018
Apolipoprotein E secreted by astrocytes forms antiparallel dimers in discoidal lipoproteins
Abstract
The Apolipoprotein E gene (APOE) is of great interest due to its role as a risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer's disease. ApoE is secreted by astrocytes in the central nervous system in high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-like lipoproteins. Structural models of lipidated ApoE of high resolution could aid in a mechanistic understanding of how ApoE functions in health and disease. Using monoclonal Fab and F(ab')2 fragments, we characterize the structure of lipidated ApoE on astrocyte-secreted lipoproteins. Our results provide support for the "double-belt" model of ApoE in nascent discoidal HDL-like lipoproteins, where two ApoE proteins wrap around the nanodisc in an antiparallel conformation. We further show that lipidated, recombinant ApoE accurately models astrocyte-secreted ApoE lipoproteins. Cryogenic electron microscopy of recombinant lipidated ApoE further supports ApoE adopting antiparallel dimers in nascent discoidal lipoproteins.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; ApoE; HDL; apolipoprotein E; astrocytes; cryo-EM; glia; lipoprotein.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests D.M.H. is an inventor on a patent licensed by Washington University to NextCure on the therapeutic use of anti-ApoE antibodies. D.M.H. co-founded and is on the scientific advisory board of C2N Diagnostics. D.M.H. is on the scientific advisory board of Denali, Genentech, and Cajal Neuroscience; consults for Asteroid; and is on the advisory board for Cell.
Figures
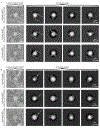
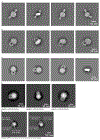

References
-
- Pitas RE, Boyles JK, Lee SH, Hui D, and Weisgraber KH (1987). Lipoproteins and their receptors in the central nervous system. Characterization of the lipoproteins in cerebrospinal fluid and identification of apolipoprotein B,E(LDL) receptors in the brain. J. Biol. Chem 262, 14352–14360. 10.1016/s0021-9258(18)47945-8. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

