Roles of extracellular matrix in lung diseases
- PMID: 38267030
- PMCID: PMC10867433
- DOI: 10.5387/fms.2023-07
Roles of extracellular matrix in lung diseases
Abstract
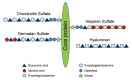
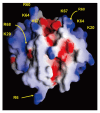
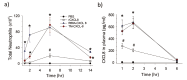
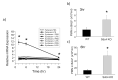
Extracellular matrix (ECM) is a non-cellular constituent found in all tissues and organs. Although ECM was previously recognized as a mere "molecular glue" that supports the tissue structure of organs such as the lungs, it has recently been reported that ECM has important biological activities for tissue morphogenesis, inflammation, wound healing, and tumor progression. Proteoglycans are the main constituent of ECM, with growing evidence that proteoglycans and their associated glycosaminoglycans play important roles in the pathogenesis of several diseases. However, their roles in the lungs are incompletely understood. Leukocyte migration into the lung is one of the main aspects involved in the pathogenesis of several lung diseases. Glycosaminoglycans bind to chemokines and their interaction fine-tunes leukocyte migration into the affected organs. This review focuses on the role chemokine and glycosaminoglycan interactions in neutrophil migration into the lung. Furthermore, this review presents the role of proteoglycans such as syndecan, versican, and hyaluronan in inflammatory and fibrotic lung diseases.
Keywords: extracellular matrix; lung fibrosis; lung inflammation; syndecan.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Versican in inflammation and tissue remodeling: the impact on lung disorders.Glycobiology. 2015 Mar;25(3):243-51. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwu120. Epub 2014 Nov 3. Glycobiology. 2015. PMID: 25371494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycosaminoglycans as key molecules in atherosclerosis: the role of versican and hyaluronan.Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(33):4018-26. doi: 10.2174/092986710793205354. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20939824 Review.
-
Interplay of extracellular matrix and leukocytes in lung inflammation.Cell Immunol. 2017 Feb;312:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2016.12.003. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Cell Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28077237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining the versican interactome in lung health and disease.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Aug 1;323(2):C249-C276. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00162.2022. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35649251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Syndecans in heart fibrosis.Cell Tissue Res. 2016 Sep;365(3):539-52. doi: 10.1007/s00441-016-2454-2. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Cell Tissue Res. 2016. PMID: 27411689 Review.
Cited by
-
Syndecan-1 as a prognostic biomarker in COVID-19 patients: a retrospective study of a Japanese cohort.Thromb J. 2024 Jun 21;22(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12959-024-00619-2. Thromb J. 2024. PMID: 38907229 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronic Acid in Immune Response.Biomolecules. 2025 Jul 14;15(7):1008. doi: 10.3390/biom15071008. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40723879 Free PMC article. Review.

