Mammalian integrated stress responses in stressed organelles and their functions
- PMID: 38267546
- PMCID: PMC11130345
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-023-01225-0
Mammalian integrated stress responses in stressed organelles and their functions
Abstract
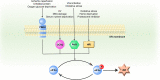
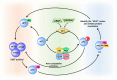
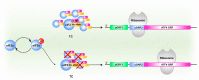
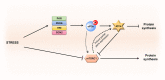
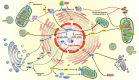
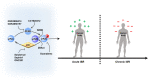
The integrated stress response (ISR) triggered in response to various cellular stress enables mammalian cells to effectively cope with diverse stressful conditions while maintaining their normal functions. Four kinases (PERK, PKR, GCN2, and HRI) of ISR regulate ISR signaling and intracellular protein translation via mediating the phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 α (eIF2α) at Ser51. Early ISR creates an opportunity for cells to repair themselves and restore homeostasis. This effect, however, is reversed in the late stages of ISR. Currently, some studies have shown the non-negligible impact of ISR on diseases such as ischemic diseases, cognitive impairment, metabolic syndrome, cancer, vanishing white matter, etc. Hence, artificial regulation of ISR and its signaling with ISR modulators becomes a promising therapeutic strategy for relieving disease symptoms and improving clinical outcomes. Here, we provide an overview of the essential mechanisms of ISR and describe the ISR-related pathways in organelles including mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. Meanwhile, the regulatory effects of ISR modulators and their potential application in various diseases are also enumerated.
Keywords: activating transcription factor 4; eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2; integrated stress response; organelles; protein homeostasis.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ISR Modulators in Neurological Diseases.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025;23(10):1184-1214. doi: 10.2174/011570159X361653250213114821. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39995125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Saturated phosphatidic acids induce mTORC1-driven integrated stress response contributing to glucolipotoxicity in hepatocytes.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2025 Jun 1;328(6):G663-G676. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00027.2025. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40241617 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the integrated stress response (ISR) pathways in response to Ref-1 inhibition in human pancreatic cancer and its tumor microenvironment.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 27;10:1146115. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1146115. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37181357 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Stress Response Potentiates Ponatinib-Induced Cardiotoxicity.Circ Res. 2024 Mar;134(5):482-501. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.323683. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Circ Res. 2024. PMID: 38323474 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the role of collided ribosomes during the activation of the integrated stress response.Biochem Soc Trans. 2025 Jun 30;53(3):615-626. doi: 10.1042/BST20253034. Biochem Soc Trans. 2025. PMID: 40440025 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Food for thought: Nutrient metabolism controlling early T cell development.Bioessays. 2025 Jan;47(1):e2400179. doi: 10.1002/bies.202400179. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Bioessays. 2025. PMID: 39504233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting host integrated stress response: lead discovery of flavonoid compounds active against coronaviruses PEDV and PDCoV.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Dec 23. doi: 10.1039/d4md00846d. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39723232 Free PMC article.
-
TIGAR Suppresses ER Stress-Induced Neuronal Injury through Targeting ATF4 Signaling in Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion.J Neurosci. 2025 Mar 26;45(13):e1406242025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1406-24.2025. J Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39919831
-
Advances in research regarding epithelial-mesenchymal transition and prostate cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 May 30;13:1583255. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1583255. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40519259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Balance of MFN2 and OPA1 in Mitochondrial Dynamics, Cellular Homeostasis, and Disease.Biomolecules. 2025 Mar 18;15(3):433. doi: 10.3390/biom15030433. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40149969 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

