TFEB and TFE3 cooperate in regulating inorganic arsenic-induced autophagy-lysosome impairment and immuno-dysfunction in primary dendritic cells
- PMID: 38267572
- PMCID: PMC10808261
- DOI: 10.1007/s10565-024-09841-0
TFEB and TFE3 cooperate in regulating inorganic arsenic-induced autophagy-lysosome impairment and immuno-dysfunction in primary dendritic cells
Abstract
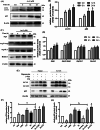
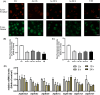
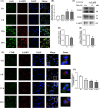
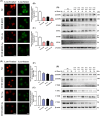
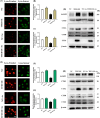
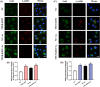
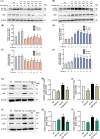
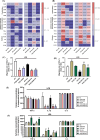
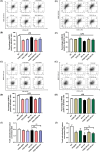
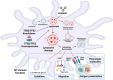
Arsenic (As) is a prevalent and hazardous environmental toxicant associated with cancer and various health problems, which has been shown suppressive effects on dendritic cells (DCs). Autophagy is essential for the innate and adaptive immune responses of DCs, and the transcription factors TFEB and TFE3 are key regulators of autophagic and lysosomal target genes. However, the detrimental alterations of the autophagy-lysosome pathway in As-exposed DCs and the possible coordinating roles of TFEB and TFE3 in the immune dysfunction of this cell are less understood. In this paper, we found that As exposure significantly impaired lysosomal number, lysosomal acidic environment, and lysosomal membrane permeabilization, which might lead to blocked autophagic flux in cultured DCs. Furthermore, our results confirmed that TFEB or TFE3 knockdown exacerbated the disorders of lysosome and the blockade of autophagic flux in As-exposed DCs, and also enhanced the inhibitory expression of co-stimulatory molecules Cd80 and Cd83; adhesion molecule Icam1; cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6; chemokine receptor Ccr7; and antigen-presenting molecules MHC II and MHC I. By contrast, overexpression of TFEB or TFE3 partially alleviated the above-mentioned impairment of DCs by inorganic As exposure. In conclusion, these findings reveal a previously unappreciated inhibition of lysosome-mediated degradation and damage of lysosomal membrane integrity leading to dysregulated autophagy and impaired immune functions of DCs by arsenicals, and also suggest TFEB and TFE3 as potential therapeutic targets for ameliorating As toxicity.
Keywords: Autophagy; Dendritic cells; Inorganic arsenic; Lysosome; TFE3; TFEB.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TFE3-mediated lysosomal biogenesis and homeostasis alleviates arsenic-induced lysosomal and immune dysfunction in macrophages.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2025 Jul 1;299:118374. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2025.118374. Epub 2025 May 22. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2025. PMID: 40409189
-
Trigonochinene E promotes lysosomal biogenesis and enhances autophagy via TFEB/TFE3 in human degenerative NP cells against oxidative stress.Phytomedicine. 2023 Apr;112:154720. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154720. Epub 2023 Feb 18. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36868108
-
Arsenic induces mTOR-dependent autophagy, whereas it impairs the autophagy-lysosome pathway and the potential role of TFEB in cultured dendritic cells.Metallomics. 2020 Aug 19;12(8):1230-1245. doi: 10.1039/d0mt00057d. Metallomics. 2020. PMID: 32519707
-
Emerging roles for TFEB in the immune response and inflammation.Autophagy. 2018;14(2):181-189. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1313943. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Autophagy. 2018. PMID: 28738171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Transcription Factor EB Links Cellular Stress to the Immune Response .Yale J Biol Med. 2017 Jun 23;90(2):301-315. eCollection 2017 Jun. Yale J Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28656016 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
mRNA vaccines in tumor targeted therapy: mechanism, clinical application, and development trends.Biomark Res. 2024 Aug 31;12(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00644-3. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39217377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy in tumor immune escape and immunotherapy.Mol Cancer. 2025 Mar 19;24(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02277-y. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40102867 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aits S. Methods to detect loss of lysosomal membrane integrity. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1880:315–29. 10.1007/978-1-4939-8873-0_21. - PubMed
-
- Bretou M, Saez PJ, Sanseau D et al. Lysosome signaling controls the migration of dendritic cells. Sci Immunol. 2017;2(16). 10.1126/sciimmunol.aak9573. - PubMed
-
- Ding J, Xie Y, Sun X, et al. Inhibition of TFEB promotes tumor-educated dendritic cells activation to enhance antitumor immune responses. Mol Immunol. 2022;147:30–9. 10.1016/j.molimm.2022.04.011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

