METTL3-mediated RanGAP1 promotes colorectal cancer progression through the MAPK pathway by recruiting YTHDF1
- PMID: 38267624
- PMCID: PMC11016466
- DOI: 10.1038/s41417-024-00731-5
METTL3-mediated RanGAP1 promotes colorectal cancer progression through the MAPK pathway by recruiting YTHDF1
Abstract
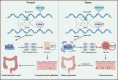
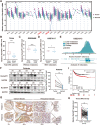
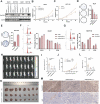
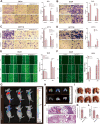
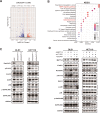
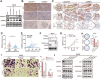
Ran GTPase activating protein 1 (RanGAP1) has been implicated in various diseases, but its role in colorectal cancer (CRC) progression remains unclear. Using tumor tissues and public databases, we found that RanGAP1 was significantly upregulated in CRC tissues and was associated with poor prognosis of patients. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) was found to play an important role in higher expression of RanGAP1. MeRIP-seq, RIP-qPCR, Luciferase reporter assays and other related experiment elucidated the molecular mechanism underlying m6A modification of RanGAP1. Besides, cell function experiments and xenograft tumor models corroborated the function of RanGAP1 in CRC progression. By RNA-seq and related analysis, RanGAP1 was verified to influent CRC progression via the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. Therefore, N6-methyladenosine modification of RanGAP1 by METTL3/YTHDF1 plays a role in CRC progression through the MAPK pathway and could be a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for CRC. Schematic diagram showed that N6-methyladenosine modification of RanGAP1 promotes CRC progression via the MAPK signaling pathway.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
METTL3/IGF2BP2 axis affects the progression of colorectal cancer by regulating m6A modification of STAG3.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 12;13(1):17292. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44379-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37828232 Free PMC article.
-
METTL3 facilitates tumor progression via an m6A-IGF2BP2-dependent mechanism in colorectal carcinoma.Mol Cancer. 2019 Jun 24;18(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1038-7. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31230592 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulated METTL3 promotes metastasis of colorectal Cancer via miR-1246/SPRED2/MAPK signaling pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Sep 6;38(1):393. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1408-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31492150 Free PMC article.
-
Review of METTL3 in colorectal cancer: From mechanisms to the therapeutic potential.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Oct;277(Pt 2):134212. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134212. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39069066 Review.
-
N6-methyladenosine-dependent signaling in colorectal cancer: Functions and clinical potential.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024 Jun;198:104360. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2024.104360. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38615872 Review.
Cited by
-
Circ_RUSC2 Sequesters miR-661 and Elevates TUSC2 Expression to Suppress Colorectal Cancer Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 24;26(7):2937. doi: 10.3390/ijms26072937. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243558 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on N6-methyladenosine and non-coding RNA in multiple myeloma.Discov Oncol. 2025 Apr 25;16(1):615. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02386-6. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40281359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of invigorating-spleen and anticancer prescription on extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in colon cancer mice model.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Nov 15;16(11):4468-4476. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i11.4468. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39554742 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

