FBXO28 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion via upregulation of the TGF-beta1/SMAD2/3 signaling pathway in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 38267923
- PMCID: PMC10807113
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-11893-8
FBXO28 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion via upregulation of the TGF-beta1/SMAD2/3 signaling pathway in ovarian cancer
Abstract
Background: Ovarian cancer is one of the most common gynecological malignancies due to the lack of early symptoms, early diagnosis and limited screening. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the molecular mechanism underlying the occurrence and progression of ovarian cancer and to identify a basic biomarker for the early diagnosis and clinical treatment of ovarian cancer.
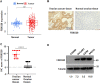
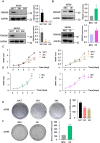
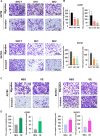
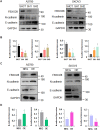
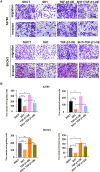
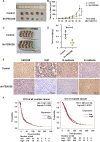
Methods: The association between FBXO28 and ovarian cancer prognosis was analyzed using Kaplan‒Meier survival analysis. The difference in FBXO28 mRNA expression between normal ovarian tissues and ovarian tumor tissues was obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), and Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) cohorts. The expression levels of the FBXO28 protein in ovarian cancer tissues and normal ovarian tissues were measured via immunohistochemical staining. Western blotting was used to determine the level of FBXO28 expression in ovarian cancer cells. The CCK-8, the colony formation, Transwell migration and invasion assays were performed to evaluate cell proliferation and motility.
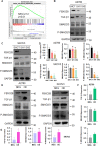
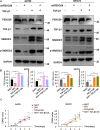
Results: We found that a higher expression level of FBXO28 was associated with poor prognosis in ovarian cancer patients. Analysis of the TCGA and GTEx cohorts showed that the FBXO28 mRNA level was lower in normal ovarian tissue samples than in ovarian cancer tissue samples. Compared with that in normal ovarian tissues or cell lines, the expression of FBXO28 was greater in ovarian tumor tissues or tumor cells. The upregulation of FBXO28 promoted the viability, proliferation, migration and invasion of ovarian cancer cells. Finally, we demonstrated that FBXO28 activated the TGF-beta1/Smad2/3 signaling pathway in ovarian cancer.
Conclusions: In conclusion, FBXO28 enhanced oncogenic function via upregulation of the TGF-beta1/Smad2/3 signaling pathway in ovarian cancer.
Keywords: FBXO28; Migration; Ovarian cancer; Smad2/3; TGF-b1.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TIPE2 inhibits the migration and invasion of epithelial ovarian cancer cells by targeting Smad2 to reverse TGF-β1-induced EMT.FASEB J. 2024 Sep;38(17):e70045. doi: 10.1096/fj.202401427R. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 39259551
-
Transcription factor specificity protein 1-mediated Serine/threonine kinase 39 upregulation promotes the proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating the transforming growth factor-β1 /Smad2/3 pathway.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):3566-3577. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1947939. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34281492 Free PMC article.
-
KLF8 is activated by TGF-β1 via Smad2 and contributes to ovarian cancer progression.J Cell Biochem. 2022 May;123(5):921-934. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30235. Epub 2022 Mar 16. J Cell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35293014
-
The TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling pathway is involved in Musashi2-induced invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer.Mol Carcinog. 2023 Feb;62(2):261-276. doi: 10.1002/mc.23484. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Mol Carcinog. 2023. PMID: 36345938
-
Role of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) on TGF-β1 signaling pathway in epithelial ovarian cancer cells.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016 Jan;142(1):47-58. doi: 10.1007/s00432-015-1998-y. Epub 2015 Jun 20. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26091707 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Silencing NEDD4L Effectively Inhibits the Malignant Behaviors of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2025 Jul 10;12:1369-1391. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S511466. eCollection 2025. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2025. PMID: 40661237 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting TGF-β: a promising strategy for cancer therapy.Med Oncol. 2025 Mar 28;42(5):142. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02667-8. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40155496 Review.
-
Exploring the multifaceted role of direct interaction between cancer cells and fibroblasts in cancer progression.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 May 28;11:1379971. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1379971. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38863965 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allemani C, Matsuda T, Di Carlo V, Harewood R, Matz M, Niksic M, Bonaventure A, Valkov M, Johnson CJ, Esteve J, et al. Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000-14 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet. 2018;391(10125):1023–75. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33326-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

