Predictors of social intermediate factors associated with sexual quality of life of women: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38267989
- PMCID: PMC10809577
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-024-02899-2
Predictors of social intermediate factors associated with sexual quality of life of women: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Sexual problems and diminished sexual quality of life can adversely affect the physical, psychological, and emotional health of women. The present study was done to determine the social intermediate factors of health associated with sexual quality of life in women of reproductive age.
Design: Systematic review and Meta-analysis.
Data sources: Embase, Web of Science, PubMed/Medline (NLM), ProQuest, and CENTRAL.
Eligibility criteria: Observational studies (cross-sectional, case-control, cohort) from 2010 to 2022 with no language constraints were included. The sexual quality of life, as the main variable of the study, has been evaluated using Symonds women's sexual quality of life scale (SQOL-F). The health social determinants intermediate factors based on WHO model were considered as exposure variables.
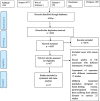
Data extraction and synthesis: The data of included studies were extracted by two independent persons through a researcher-made checklist according to the study aims. Quality assessment of studies was done using Newcastle-Ottawa instrument. R software (Version R-4.2.1) were used for meta-analysis. Publication bias was evaluated by Egger & Begg tests. Sensitivity analysis was done through one-out remove approach.
Results: Eventually, 15 studies were eligible to be included in this systematic review and meta-analysis. Variables of depression, quality of marital relation, body image, self-esteem, physical activity, and sexual function were among the health social intermediate factors associated with sexual quality of life. Publication bias had no effect on the obtained results; no study affecting the results was found through sensitivity analysis.
Conclusion: Considering the relationship between modifiable factors and sexual quality of life, it seems that identification of these factors can be an important step towards designing interventional studies to help women experience enhanced sexual quality of life.
Keywords: Sexual health; Social determinants of health; Systematic review and meta-analysis; Women.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
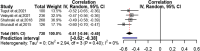
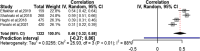

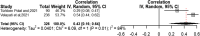
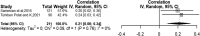
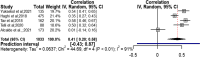

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

